The Dysferlin C2A Domain Binds PI(4,5)P2 and Penetrates Membranes
- PMID: 37406927
- PMCID: PMC10699586
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2023.168193
The Dysferlin C2A Domain Binds PI(4,5)P2 and Penetrates Membranes
Abstract
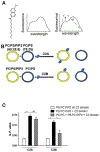
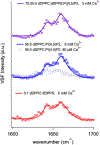
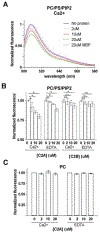
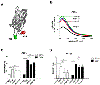
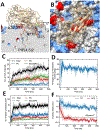
Dysferlin is a large membrane protein found most prominently in striated muscle. Loss of dysferlin activity is associated with reduced exocytosis, abnormal intracellular Ca2+ and the muscle diseases limb-girdle muscular dystrophy and Miyoshi myopathy. The cytosolic region of dysferlin consists of seven C2 domains with mutations in the C2A domain at the N-terminus resulting in pathology. Despite the importance of Ca2+ and membrane binding activities of the C2A domain for dysferlin function, the mechanism of the domain remains poorly characterized. In this study we find that the C2A domain preferentially binds membranes containing PI(4,5)P2 through an interaction mediated by residues Y23, K32, K33, and R77 on the concave face of the domain. We also found that subsequent to membrane binding, the C2A domain inserts residues on the Ca2+ binding loops into the membrane. Analysis of solution NMR measurements indicate that the domain inhabits two distinct structural states, with Ca2+ shifting the population between states towards a more rigid structure with greater affinity for PI(4,5)P2. Based on our results, we propose a mechanism where Ca2+ converts C2A from a structurally dynamic, low PI(4,5)P2 affinity state to a high affinity state that targets dysferlin to PI(4,5)P2 enriched membranes through interaction with Tyr23, K32, K33, and R77. Binding also involves changes in lipid packing and insertion by the third Ca2+ binding loop of the C2 domain into the membrane, which would contribute to dysferlin function in exocytosis and Ca2+ regulation.
Keywords: C2 domain; CEST; calcium; dysferlin; genetic code expansion.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

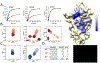

References
-
- Lek A, Evesson FJ, Sutton RB, North KN, Cooper ST (2012) Ferlins: Regulators of Vesicle Fusion for Auditory Neurotransmission, Receptor Trafficking and Membrane Repair. Traffic 13(2):185–194. - PubMed
-
- Bansal D, Campbell KP (2004) Dysferlin and the plasma membrane repair in muscular dystrophy. Trends Cell Biol 14(4):206–213. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

