Reproducibility of Deep Learning Algorithms Developed for Medical Imaging Analysis: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 37407841
- PMCID: PMC10501962
- DOI: 10.1007/s10278-023-00870-5
Reproducibility of Deep Learning Algorithms Developed for Medical Imaging Analysis: A Systematic Review
Abstract
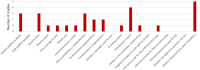
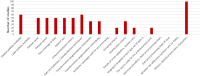
Since 2000, there have been more than 8000 publications on radiology artificial intelligence (AI). AI breakthroughs allow complex tasks to be automated and even performed beyond human capabilities. However, the lack of details on the methods and algorithm code undercuts its scientific value. Many science subfields have recently faced a reproducibility crisis, eroding trust in processes and results, and influencing the rise in retractions of scientific papers. For the same reasons, conducting research in deep learning (DL) also requires reproducibility. Although several valuable manuscript checklists for AI in medical imaging exist, they are not focused specifically on reproducibility. In this study, we conducted a systematic review of recently published papers in the field of DL to evaluate if the description of their methodology could allow the reproducibility of their findings. We focused on the Journal of Digital Imaging (JDI), a specialized journal that publishes papers on AI and medical imaging. We used the keyword "Deep Learning" and collected the articles published between January 2020 and January 2022. We screened all the articles and included the ones which reported the development of a DL tool in medical imaging. We extracted the reported details about the dataset, data handling steps, data splitting, model details, and performance metrics of each included article. We found 148 articles. Eighty were included after screening for articles that reported developing a DL model for medical image analysis. Five studies have made their code publicly available, and 35 studies have utilized publicly available datasets. We provided figures to show the ratio and absolute count of reported items from included studies. According to our cross-sectional study, in JDI publications on DL in medical imaging, authors infrequently report the key elements of their study to make it reproducible.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Deep learning; Machine learning; Medical imaging; Reproducibility.
© 2023. The Author(s) under exclusive licence to Society for Imaging Informatics in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Arbabshirani MR, Fornwalt BK, Mongelluzzo GJ, Suever JD, Geise BD, Patel AA, et al. Advanced machine learning in action: identification of intracranial hemorrhage on computed tomography scans of the head with clinical workflow integration. NPJ Digit Med. 2018;1:9. doi: 10.1038/s41746-017-0015-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

