HDV RNA Levels and Progression of Hepatitis Delta Infection: A 14 Year Follow Up Experience in Italy
- PMID: 37408247
- PMCID: PMC10217045
- DOI: 10.3390/cells12101413
HDV RNA Levels and Progression of Hepatitis Delta Infection: A 14 Year Follow Up Experience in Italy
Abstract
Background: Identification of outcome predictors is one of the unmet needs in chronic HDV infection. Until recently, no reliable quantitative assays for HDV RNA were available.
Aims: To evaluate the impact of baseline viremia on natural history of HDV infection in a cohort of patients whose serum samples were stored at their first visit 15 years ago.
Methods: Quantitative HBsAg, HBeAg, HBeAb, HBV DNA, HDV RNA, genotypes, and liver disease severity were assessed at baseline. Patients who were no longer on active follow-up were recalled and re-evaluated in August 2022.
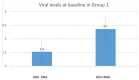
Results: The majority of patients were male (64.9%); the median age was 50.1 years; and all patients were Italian, with only three born in Romania. All were HBeAg negative with HBV genotype D infection. Patients were subdivided three groups: 23 were in active follow-up (Group 1), 21 were recalled due to no longer being in follow-up (Group 2), and 11 died (Group 3). Liver cirrhosis was diagnosed in 28 subjects at the first visit; 39.3% of diagnosed patients were in Group 3, 32.1% were in Group 1 and 28.6% were in Group 2 (p = 0.001). Baseline HBV DNA IU/mL Log10 were 1.6 (1.0-5.9) in Group 1, 1.3 (1.0-4.5) in Group 2, and 4.1 (1.5-4.5) in Group 3; median baseline HDV RNA Log10 levels were 4.1 (0.7-6.7) in Group 1, 3.2 (0.7-6.2) in Group 2, and 5.2 (0.7-6.7) in Group 3, resulting significantly higher rates among patients in Group 3 compared to the other groups (p = 0.038). Eighteen patients in Group 2, as compared to 7 in Group 1, had undetectable HDV RNA at the follow-up evaluation (p = 0.001).
Conclusions: HDV chronic infection is a heterogeneous disease. It may not only progress but also improve over time in patients, who eventually become HDV RNA-undetectable. HDV RNA levels may help identify the subgroup of patients with less progressive liver disease.
Keywords: HBV DNA; cirrhosis; quantitative HBsAg; quantitative HDV RNA.
Conflict of interest statement
A.M. has served as speaker for BMS, Gilead Sciences, Janssen and MSD. All the other Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Rizzetto M., Hepatitis D. Virus. In: Wong E.J., Gish R.G., editors. Clinical Epidemiology of Chronic Liver Diseases. Springer Nature; Cham, Switzerland: 2019. pp. 135–148.
-
- Stroffolini T., Morisco F., Ferrigno L., Pontillo G., Iantosca G., Cossiga V., Crateri S., Tosti M.E. Acute Delta Hepatitis in Italy spanning three decades (1991–2019): Evidence for the effectiveness of the hepatitis B vaccination campaign. J. Viral. Hepat. 2022;29:78–86. doi: 10.1111/jvh.13620. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical