Strategies to Prevent Mother-to-child Transmission of Hepatitis B Virus
- PMID: 37408824
- PMCID: PMC10318275
- DOI: 10.14218/JCTH.2022.00332
Strategies to Prevent Mother-to-child Transmission of Hepatitis B Virus
Abstract
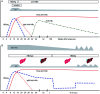
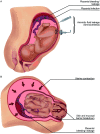
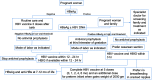
Mother-to-child transmission (MTCT) of hepatitis B virus (HBV) is the primary cause of chronic HBV infection worldwide. MTCT prevention and antiviral treatment of infected individuals could eliminate this public health burden. Antiviral treatment of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg)-positive pregnant women and immunoprophylaxis with HBV vaccine and hepatitis B immune globulin are the most effective strategies to interfere with MTCT of HBV. However, for worldwide application of those strategies, feasibility, availability, cost, safety, and effectiveness should be considered. Cesarean section and breastfeeding avoidance in hepatitis B e antigen-positive mothers with a high viral load and without antiviral therapy during pregnancy could be an option, but more supporting evidence is needed. HBsAg screening of all pregnant women is recommended when initiating antiviral therapy and immunoprophylaxis for MTCT prevention, except in areas with limited resources. Timely HBV vaccination series administered soon after birth might be the mainstay of prevention. This review aimed to provide a concise update on the effectiveness of available strategies to prevent MTCT of HBV.
Keywords: Children; Hepatitis B virus; Mother-to-child transmission; Prevention; Vaccine; Vertical transmission.
© 2023 Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interests related to this publication.
Figures
References
-
- Prevention of Mother-to-Child Transmission of Hepatitis B Virus: Guidelines on Antiviral Prophylaxis in Pregnancy. Geneva: World Health Organization 2020. - PubMed
-
- Pan YC, Jia ZF, Wang YQ, Yang N, Liu JX, Zhai XJ, et al. The role of caesarean section and nonbreastfeeding in preventing mother-to-child transmission of hepatitis B virus in HBsAg-and HBeAg-positive mothers: results from a prospective cohort study and a meta-analysis. J Viral Hepat. 2020;27(10):1032–1043. doi: 10.1111/jvh.13314. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pan YC, Jia ZF, Wu YH, Lv HY, Jiang J. Response to comments on: The role of caesarean section and nonbreastfeeding in preventing mother-to-child transmission of hepatitis B virus in HBsAg- and HBeAg-positive mothers: results from a prospective cohort study and a meta-analysis. J Viral Hepat. 2022;29(3):235–236. doi: 10.1111/jvh.13642. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
