Case Report: Longitudinal follow-up and testicular sperm extraction in a patient with a pathogenic NR5A1 (SF-1) frameshift variant: p.(Phe70Ser fs*5)
- PMID: 37409232
- PMCID: PMC10319352
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1171822
Case Report: Longitudinal follow-up and testicular sperm extraction in a patient with a pathogenic NR5A1 (SF-1) frameshift variant: p.(Phe70Ser fs*5)
Abstract
Background: Steroidogenic factor 1 (SF-1), encoded by the nuclear receptor subfamily 5 group A member 1 (NR5A1) gene, is a transcriptional factor crucial for adrenal and gonadal organogenesis. Pathogenic variants of NR5A1 are responsible for a wide spectrum of phenotypes with autosomal dominant inheritance including disorders of sex development and oligospermia-azoospermia in 46,XY adults. Preservation of fertility remains challenging in these patients.
Objective: The aim was to offer fertility preservation at the end of puberty in an NR5A1 mutated patient.
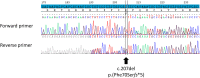
Case report: The patient was born of non-consanguineous parents, with a disorder of sex development, a small genital bud, perineal hypospadias, and gonads in the left labioscrotal fold and the right inguinal region. Neither uterus nor vagina was detected. The karyotype was 46,XY. Anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) and testosterone levels were low, indicating testicular dysgenesis. The child was raised as a boy. At 9 years old, he presented with precocious puberty treated by triptorelin. At puberty, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinising hormone (LH), and testosterone levels increased, whereas AMH, inhibin B, and testicular volume were low, suggesting an impaired Sertoli cell function and a partially preserved Leydig cell function. A genetic study performed at almost 15 years old identified the new frameshift variant NM_004959.5: c.207del p.(Phe70Serfs*5) at a heterozygous state. He was thus addressed for fertility preservation. No sperm cells could be retrieved from three semen collections between the ages of 16 years 4 months and 16 years 10 months. A conventional bilateral testicular biopsy and testicular sperm extraction were performed at 17 years 10 months of age, but no sperm cells were found. Histological analysis revealed an aspect of mosaicism with seminiferous tubules that were either atrophic, with Sertoli cells only, or presenting an arrest of spermatogenesis at the spermatocyte stage.
Conclusion: We report a case with a new NR5A1 variant. The fertility preservation protocol proposed at the end of puberty did not allow any sperm retrieval for future parenthood.
Keywords: azoospermia; congenital; disorder of sex development; gonadal dysgenesis; hypospadias; male infertility; spermatogenesis; testicular sperm extraction.
Copyright © 2023 Teoli, Mallet, Renault, Gay, Labrune, Bretones, Giscard D’Estaing, Cuzin, Dijoud, Roucher-Boulez and Plotton.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

