Preliminary study of anti-CD40 and ubiquitin proteasome antibodies in primary podocytopaties
- PMID: 37409273
- PMCID: PMC10319126
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1189017
Preliminary study of anti-CD40 and ubiquitin proteasome antibodies in primary podocytopaties
Abstract
Background: Minimal change disease and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis are primary podocytopathies that are clinically presented in adults presenting with severe nephrotic syndrome. The pathogenesis of these diseases is not clear and many questions remain to be answered. A new concept about the role of changes in the antigenic determinant of podocytes and the production of anti-podocyte antibodies that cause podocyte damage is being developed. The aim of the study is to evaluate the levels of anti-CD40 and anti-ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase L1 (anti-UCH-L1) antibodies in patients with podocytopathies in comparison with other glomerulopathies.
Methods: One hundred and six patients with glomerulopathy and 11 healthy subjects took part in the study. A histological study revealed primary FSGS in 35 patients (genetic cases of FSGS and secondary FSGS in the absence of NS were excluded), 15 had MCD, 21 - MN, 13 - MPGN, 22 patients - IgA nephropathy. The effect of steroid therapy was evaluated in patients with podocytopathies (FSGS and MCD). The serum levels of anti-UCH-L1 and anti-CD40 antibodies were measured by ELISA before steroid treatment.
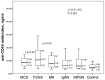
Results: The levels of anti-UCH-L1 antibodies were significantly higher in MCD patients and anti-CD40 antibodies were higher in MCD and FSGS than in the control group and other groups of glomerulopathies. In addition, the level of anti-UCH-L1 antibodies was higher in patients with steroid-sensitive FSGS and MCD, and anti-CD40 antibodies were lower than in patients with steroid-resistant FSGS. An increase in anti-UCH-L1 antibody levels above 6.44 ng/mL may be a prognostic factor of steroid-sensitivity. The ROC curve (AUC = 0.875 [95% CI 0.718-0.999]) for response to therapy showed a sensitivity of 75% and specificity of 87.5%.
Conclusion: An increase in the level of anti-UCH-L1 antibodies is specific for steroid-sensitive FSGS and MCD, while an increase in anti-CD40 antibodies - for steroid-resistant FSGS, compared with other glomerulopathies. It suggests that these antibodies could be a potential factor for differential diagnosis and treatment prognosis.
Keywords: FSGS; anti-CD40 antibodies; anti-UCH-L1 antibodies; minimal change disease; podocytopathy.
Copyright © 2023 Chebotareva, Cao, Vinogradov, Alentov, Sergeeva, Kononikhin and Moiseev.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Sharma M, Zhou J, Gauchat J, Sharma R, McCarthy ET, Srivastava T, et al. Janus kinase 2/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 inhibitors attenuate the effect of cardiotrophin-like cytokine factor 1 and human focal segmental glomerulosclerosis serum on glomerular filtration barrier. Transl Res. (2015) 166:384–98. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2015.03.002 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

