Assessing the Effectiveness of Qista Baited Traps in Capturing Mosquito Vectors of Diseases in the Camargue Region (France) and Investigating Their Diversity
- PMID: 37409687
- PMCID: PMC10251931
- DOI: 10.3390/ani13111809
Assessing the Effectiveness of Qista Baited Traps in Capturing Mosquito Vectors of Diseases in the Camargue Region (France) and Investigating Their Diversity
Abstract
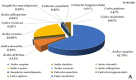
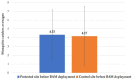
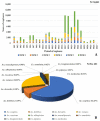
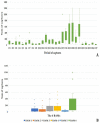
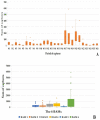
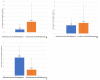
Nuisance, allergy, and vector role: mosquitoes are responsible for numerous inconveniences. Several strategies have been employed to fight against this confirmed vector. To record the diversity of mosquito vectors in Camargue (France) and assess the effectiveness of the Qista trap, six BAMs were deployed as a belt barrier to protect the Espeyran Castle (Saint-Gilles, Camargue). Prior to evaluating the reduction in the nuisance rate, recovery nets from the traps and human landing catches (HLC) were utilized twice a week in the treated and control areas. Overall, 85,600 mosquitoes were captured, belonging to eleven species, namely Aedes albopictus, Aedes caspius, Aedes detritus, Aedes dorsalis, Aedes rossicus, Aedes vexans, Anopheles maculipennis, Culex pipiens, Culex modestus, Culiseta annulata and Culiseta longiareolata. The six BAM devices trapped 84,461 mosquitoes. The average capture rate per BAM is 76.92 mosquitoes per day. The rate of nuisance has decreased from 4.33 ± 2.88 before the deployment to 1.59 ± 2.77 after BAM implantation. The Qista BAM trap seems to be an excellent tool for reducing the nuisance rate and may help researchers to optimize trapping methods by obtaining more significant sample sizes. It may also allow the updating of the host-seeking mosquito species' reported biodiversity in the south of France.
Keywords: BAM; France; QISTA; Saint-Gilles; mosquito.
Conflict of interest statement
Three authors declare the following financial statement that may be considered potential competing interests: H.L. and A.C.C. are QISTA employees. C.B. joined the Qista company at the end of the experiment. M.B., I.L. and C.R. declared no competing interests and did not receive any financial compensation from Qista.
Figures




References
-
- Harbach R.E. The Culicidae (Diptera): A review of taxonomy, classification and phylogeny. Zootaxa. 2007;1668:591–638. doi: 10.11646/zootaxa.1668.1.28. - DOI
-
- Harbach R. Culicidae Meigen, 1818. Mosquito Taxonomic Inventory. [(accessed on 15 March 2023)]. Available online: https://mosquito-taxonomic-inventory.myspecies.info/simpletaxonomy/term/....
-
- Becker N., Petric D., Zgomba M., Boase C., Madon M., Dahl C., Kaiser A. Mosquitoes and Their Control. Springer Science & Business Media; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2010.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

