A simple mechanism for integration of quorum sensing and cAMP signalling in Vibrio cholerae
- PMID: 37410076
- PMCID: PMC10328515
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.86699
A simple mechanism for integration of quorum sensing and cAMP signalling in Vibrio cholerae
Abstract
Many bacteria use quorum sensing to control changes in lifestyle. The process is regulated by microbially derived 'autoinducer' signalling molecules, that accumulate in the local environment. Individual cells sense autoinducer abundance, to infer population density, and alter their behaviour accordingly. In Vibrio cholerae, quorum-sensing signals are transduced by phosphorelay to the transcription factor LuxO. Unphosphorylated LuxO permits expression of HapR, which alters global gene expression patterns. In this work, we have mapped the genome-wide distribution of LuxO and HapR in V. cholerae. Whilst LuxO has a small regulon, HapR targets 32 loci. Many HapR targets coincide with sites for the cAMP receptor protein (CRP) that regulates the transcriptional response to carbon starvation. This overlap, also evident in other Vibrio species, results from similarities in the DNA sequence bound by each factor. At shared sites, HapR and CRP simultaneously contact the double helix and binding is stabilised by direct interaction of the two factors. Importantly, this involves a CRP surface that usually contacts RNA polymerase to stimulate transcription. As a result, HapR can block transcription activation by CRP. Thus, by interacting at shared sites, HapR and CRP integrate information from quorum sensing and cAMP signalling to control gene expression. This likely allows V. cholerae to regulate subsets of genes during the transition between aquatic environments and the human host.
Keywords: Vibrio cholerae; bacteria; chromosomes; cyclic amp; gene expression; quorum sensing; transcription.
© 2023, Walker et al.
Conflict of interest statement
LW, JH, JV, TD, AD, DG No competing interests declared
Figures



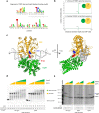
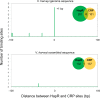
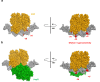
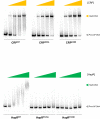


Update of
-
A simple mechanism for integration of quorum sensing and cAMP signalling in V. cholerae.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 May 26:2023.02.08.527633. doi: 10.1101/2023.02.08.527633. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Elife. 2023 Jul 06;12:RP86699. doi: 10.7554/eLife.86699. PMID: 36798193 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
A simple mechanism for integration of quorum sensing and cAMP signalling in V. cholerae.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 May 26:2023.02.08.527633. doi: 10.1101/2023.02.08.527633. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Elife. 2023 Jul 06;12:RP86699. doi: 10.7554/eLife.86699. PMID: 36798193 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
The cyclic AMP receptor protein modulates quorum sensing, motility and multiple genes that affect intestinal colonization in Vibrio cholerae.Microbiology (Reading). 2007 Sep;153(Pt 9):2964-2975. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2007/006668-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2007. PMID: 17768239
-
Regulatory targets of quorum sensing in Vibrio cholerae: evidence for two distinct HapR-binding motifs.Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 May;37(8):2747-56. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp121. Epub 2009 Mar 10. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 19276207 Free PMC article.
-
Quorum Sensing Gene Regulation by LuxR/HapR Master Regulators in Vibrios.J Bacteriol. 2017 Sep 5;199(19):e00105-17. doi: 10.1128/JB.00105-17. Print 2017 Oct 1. J Bacteriol. 2017. PMID: 28484045 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacterial quorum-sensing network architectures.Annu Rev Genet. 2009;43:197-222. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-102108-134304. Annu Rev Genet. 2009. PMID: 19686078 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A comparative genomic and phenotypic study of Vibrio cholerae model strains using hybrid sequencing.Microbiology (Reading). 2024 Sep;170(9):001502. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.001502. Microbiology (Reading). 2024. PMID: 39311857 Free PMC article.
-
Coordination of cell envelope biology by Escherichia coli MarA protein potentiates intrinsic antibiotic resistance.PLoS Genet. 2025 May 5;21(5):e1011639. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011639. eCollection 2025 May. PLoS Genet. 2025. PMID: 40324004 Free PMC article.
-
cAMP-independent DNA binding of the CRP family protein DdrI from Deinococcus radiodurans.mBio. 2024 Jul 17;15(7):e0114424. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01144-24. Epub 2024 Jun 25. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38916345 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription activation in Escherichia coli and Salmonella.EcoSal Plus. 2024 Dec 12;12(1):eesp00392020. doi: 10.1128/ecosalplus.esp-0039-2020. Epub 2024 Feb 12. EcoSal Plus. 2024. PMID: 38345370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quorum sensing in Vibrio controls carbon metabolism to optimize growth in changing environmental conditions.PLoS Biol. 2024 Nov 11;22(11):e3002891. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002891. eCollection 2024 Nov. PLoS Biol. 2024. PMID: 39527643 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Borisova M, Gaupp R, Duckworth A, Schneider A, Dalügge D, Mühleck M, Deubel D, Unsleber S, Yu W, Muth G, Bischoff M, Götz F, Mayer C. Peptidoglycan recycling in gram-positive bacteria is crucial for survival in stationary phase. MBio. 2016;7:e00923-16. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00923-16. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R35 GM128674/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- BB/N005961/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- R35GM128674/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- BB/M01116X/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- project reference 1898542/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

