Vitamin D level regulates serum lipids discrepantly in adults with and without dyslipidemia
- PMID: 37410091
- PMCID: PMC10448594
- DOI: 10.1530/EC-23-0013
Vitamin D level regulates serum lipids discrepantly in adults with and without dyslipidemia
Abstract
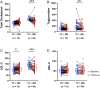
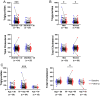
Vitamin D deficiency is associated with hyperlipidemia, but it remains unclear whether vitamin D supplementation reduces serum lipid levels. The aims of this study were to investigate the associations between increased serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) concentrations and lipid levels and identify the characteristics of people with or without lipid reduction associated with increased 25(OH)D levels. The medical records of 118 individuals (53 men; mean age, 54.4 ± 10.6 years) whose serum 25(OH)D levels increased between 2 consecutive measurements were retrospectively reviewed. People with increased 25(OH)D levels (from 22.7 (17.6-29.2) to 32.1 (25.6-36.8) mg/dL; P < 0.01) had a significant reduction in serum levels of triglycerides (TGs) (from 111.0 (80-164) to 104.5 (73-142) mg/dL; P < 0.01) and total cholesterol (TC) (from 187.5 (155-213) to 181.0 (150-210) mg/dL; P < 0.05). The individuals who responded to vitamin D (≥10% reduction in TG or TC levels) exhibited significantly higher baseline TG and TC levels than those who did not. Only patients with hyperlipidemia (not those without hyperlipidemia) at baseline exhibited significantly reduced TG and TC levels at follow-up. However, increasing serum 25(OH)D concentrations were significantly correlated with decreasing lipid levels in individuals with baseline 25(OH)D levels less than 30 ng/mL and in individuals aged 50-65 years (not in patients younger than 50 years or older than 65 years). In conclusion, increasing serum 25(OH)D concentrations may be potentially helpful for the treatment of hyperlipidemia in people with vitamin D deficiency.
Keywords: age; cholesterol; lipid; triglycerides; vitamin D.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have declared that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Association between early pregnancy vitamin D status and changes in serum lipid profiles throughout pregnancy.Metabolism. 2017 May;70:85-97. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2017.02.004. Epub 2017 Feb 12. Metabolism. 2017. PMID: 28403948
-
The Associations of Serum Lipids with Vitamin D Status.PLoS One. 2016 Oct 21;11(10):e0165157. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0165157. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27768777 Free PMC article.
-
Serum vitamin D and change in lipid levels over 5 y: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study.Nutrition. 2017 Jun;38:85-93. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2017.01.008. Epub 2017 Feb 3. Nutrition. 2017. PMID: 28526388 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D is negatively associated with triglyceride in overweight/obese patients with type 2 diabetes.Endocrine. 2022 May;76(2):304-311. doi: 10.1007/s12020-022-03009-8. Epub 2022 Mar 5. Endocrine. 2022. PMID: 35247144
-
Vitamin D and metabolic health with special reference to the effect of vitamin D on serum lipids.Prog Lipid Res. 2011 Oct;50(4):303-12. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2011.05.001. Epub 2011 May 27. Prog Lipid Res. 2011. PMID: 21640757 Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of dietary fats intake and lipid profile in Chilean patients with glucose transport type 1 deficiency syndrome: similarities and differences with the reviewed literature.Front Nutr. 2024 May 16;11:1390799. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1390799. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38818131 Free PMC article.
-
A novel LC-MS/MS method combined with derivatization for simultaneous quantification of vitamin D metabolites in human serum with diabetes as well as hyperlipidemia.RSC Adv. 2023 Nov 22;13(48):34157-34166. doi: 10.1039/d3ra05700c. eCollection 2023 Nov 16. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 38020011 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D and Dyslipidemia: Is There Really a Link? A Narrative Review.Nutrients. 2024 Apr 12;16(8):1144. doi: 10.3390/nu16081144. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38674837 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Saturation association between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and mortality in elderly people with hyperlipidemia: a population-based study from the NHANES (2001-2016).Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Oct 2;15:1382419. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1382419. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39415789 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Martins D Wolf M Pan D Zadshir A Tareen N Thadhani R Felsenfeld A Levine B Mehrotra R & Norris K. Prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors and the serum levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D in the United States: data from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Archives of Internal Medicine 20071671159–1165. (10.1001/archinte.167.11.1159) - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

