Diabetes of the Exocrine Pancreas: Implications for Pharmacological Management
- PMID: 37410209
- PMCID: PMC10361873
- DOI: 10.1007/s40265-023-01913-5
Diabetes of the Exocrine Pancreas: Implications for Pharmacological Management
Abstract
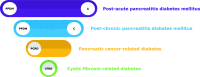
Post-pancreatitis diabetes mellitus, pancreatic cancer-related diabetes, and cystic fibrosis-related diabetes are often underappreciated. As a result, a substantial proportion of people with these sub-types of diabetes receive antidiabetic medications that may be suboptimal, if not harmful, in the context of their underlying disease of the exocrine pancreas. The present article delineates both classical (biguanides, insulin, sulfonylureas, α-glucosidase inhibitors, thiazolidinediones, and meglitinides) and newer (glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, amylin analogs, dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors, sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors, D2 receptor agonists, bile acid sequestrants, and dual glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor co-agonists) therapies and provides recommendations for managing people with diabetes of the exocrine pancreas based on the most up-to-date clinical evidence. Also, several emerging directions (lipid-enriched pathways, Y4 receptor agonism, glucagon-like peptide-1 and glucagon receptor co-agonism) are presented with a view to informing the process of new drug discovery and development.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
MOG has severed on advisory boards to Nestle Health Science and Organon. MSP has no conflicts to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cost Effectiveness of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors, Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) Receptor Agonists, and Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 (DPP-4) Inhibitors: A Systematic Review.Pharmacoeconomics. 2019 Jun;37(6):777-818. doi: 10.1007/s40273-019-00774-9. Pharmacoeconomics. 2019. PMID: 30854589
-
Sex Differences in Cardiovascular Effectiveness of Newer Glucose-Lowering Drugs Added to Metformin in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.J Am Heart Assoc. 2020 Jan 7;9(1):e012940. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.012940. Epub 2020 Jan 4. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020. PMID: 31902326 Free PMC article.
-
Myocardial infarction in type 2 diabetes using sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors, dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors or glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists: proportional hazards analysis by deep neural network based machine learning.Curr Med Res Opin. 2020 Mar;36(3):403-409. doi: 10.1080/03007995.2019.1706043. Epub 2020 Jan 6. Curr Med Res Opin. 2020. PMID: 31855074
-
Incretin-based therapies for type 2 diabetes mellitus: a review of direct comparisons of efficacy, safety and patient satisfaction.Int J Clin Pharm. 2013 Apr;35(2):159-72. doi: 10.1007/s11096-012-9729-9. Epub 2012 Dec 22. Int J Clin Pharm. 2013. PMID: 23263796 Review.
-
Updates of incretin-related drugs for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.J Diabetes Investig. 2023 Feb;14(2):189-192. doi: 10.1111/jdi.13945. Epub 2022 Nov 14. J Diabetes Investig. 2023. PMID: 36373430 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The effect of incretin-based drugs on the riks of acute pancreatitis: a review.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2024 May 5;23(1):487-495. doi: 10.1007/s40200-024-01430-6. eCollection 2024 Jun. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2024. PMID: 38932809 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dietary Fibre for the Prevention of Post-Pancreatitis Diabetes Mellitus: A Review of the Literature and Future Research Directions.Nutrients. 2024 Feb 1;16(3):435. doi: 10.3390/nu16030435. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38337719 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment outcomes with oral anti-hyperglycaemic therapies in people with diabetes secondary to a pancreatic condition (type 3c diabetes): A population-based cohort study.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2025 Mar;27(3):1544-1553. doi: 10.1111/dom.16163. Epub 2025 Jan 6. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2025. PMID: 39762966 Free PMC article.
-
Risk and factors determining diabetes after mild, nonnecrotizing acute pancreatitis.Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2024 Sep 1;40(5):396-403. doi: 10.1097/MOG.0000000000001055. Epub 2024 Jun 26. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38935336 Review.
-
Glycemic Variability in Pancreatogenic Diabetes Mellitus: characteristics, Risks, Potential Mechanisms, and Treatment Possibilities.Int J Gen Med. 2024 Sep 21;17:4297-4309. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S477497. eCollection 2024. Int J Gen Med. 2024. PMID: 39324147 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT). Design and methodologic considerations for the feasibility phase. The DCCT Research Group. Diabetes. 1986;35:530-45. - PubMed
-
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS). VIII. Study design, progress and performance. Diabetologia. 1991;34:877-90. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

