Llamas use social information from conspecifics and humans to solve a spatial detour task
- PMID: 37410341
- PMCID: PMC10442258
- DOI: 10.1007/s10071-023-01808-8
Llamas use social information from conspecifics and humans to solve a spatial detour task
Abstract
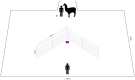
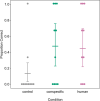
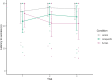
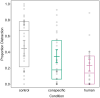
Learning by observing others (i.e. social learning) is an important mechanism to reduce the costs of individual learning. Social learning can occur between conspecifics but also heterospecifics. Domestication processes might have changed the animals' sensitivity to human social cues and recent research indicates that domesticated species are particularly good in learning socially from humans. Llamas (Lama glama) are an interesting model species for that purpose. Llamas were bred as pack animals, which requires close contact and cooperative behaviour towards humans. We investigated whether llamas learn socially from trained conspecifics and humans in a spatial detour task. Subjects were required to detour metal hurdles arranged in a V-shape to reach a food reward. Llamas were more successful in solving the task after both a human and a conspecific demonstrated the task compared to a control condition with no demonstrator. Individual differences in behaviour (i.e. food motivation and distraction) further affected the success rate. Animals did not necessarily use the same route as the demonstrators, thus, indicating that they adopted a more general detour behaviour. These results suggest that llamas can extract information from conspecific and heterospecific demonstrations; hence, broadening our knowledge of domesticated species that are sensitive to human social behaviour.
Keywords: Domestication; Emulation; Human demonstration; New world camelids; Social learning; Stimulus enhancement.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
The authors have no financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dairy cows did not rely on social learning mechanisms when solving a spatial detour task.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Sep 7;9:956559. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.956559. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 36157180 Free PMC article.
-
Horses fail to use social learning when solving spatial detour tasks.Anim Cogn. 2015 Jul;18(4):847-54. doi: 10.1007/s10071-015-0852-6. Epub 2015 Feb 26. Anim Cogn. 2015. PMID: 25716720
-
Conspecific and heterospecific information use in bumblebees.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e31444. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031444. Epub 2012 Feb 8. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22347479 Free PMC article.
-
From whom do animals learn? A meta-analysis on model-based social learning.Psychon Bull Rev. 2023 Jun;30(3):863-881. doi: 10.3758/s13423-022-02236-4. Epub 2023 Jan 6. Psychon Bull Rev. 2023. PMID: 36609963 Review.
-
[The feeding of New World camelids. Practical information for the feeding of llamas (Lama glama) and alpacas (Lama pacos)].Tierarztl Prax. 1992 Aug;20(4):435-8. Tierarztl Prax. 1992. PMID: 1329266 Review. German. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Haematology and biochemistry in healthy llamas at sea level.Vet Res Commun. 2024 Apr;48(2):1253-1256. doi: 10.1007/s11259-023-10285-w. Epub 2023 Dec 18. Vet Res Commun. 2024. PMID: 38105361
References
-
- Avarguès-Weber A, Dawson EH, Chittka L. Mechanisms of social learning across species boundaries. J Zool. 2013;290:1–11. doi: 10.1111/jzo.12015. - DOI
-
- Bates D, Maechler M, BolkerWalker BS. Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J Stat Softw. 2015;67:1–48. doi: 10.18637/jss.v067.i01. - DOI
-
- Brooks ME, Kristensen K, van Benthem KJ, Magnusson A, Berg CW, Nielsen A, Skaug HJ, Maechler M, Bolker BM. glmmTMB balances speed and flexibility among packages for zero-inflated generalized linear mixed modeling. The R Journal. 2017;9(2):378–400. doi: 10.32614/RJ-2017-066. - DOI
-
- Browman DL. Pastoral nomadism in the central andes. Curr Anthropol. 1974;15(2):188–196. doi: 10.2307/j.ctvdjrq8t.9. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

