PearMODB: a multiomics database for pear (Pyrus) genomics, genetics and breeding study
- PMID: 37410918
- PMCID: PMC10325485
- DOI: 10.1093/database/baad050
PearMODB: a multiomics database for pear (Pyrus) genomics, genetics and breeding study
Abstract
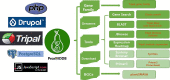
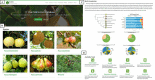
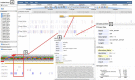
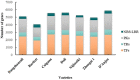
Pear (Pyrus ssp.) belongs to Rosaceae and is an important fruit tree widely cultivated around the world. Currently, challenges to cope with the burgeoning sets of multiomics data are rapidly increasing. Here, we constructed the Pear Multiomics Database (PearMODB) by integrating genome, transcriptome, epigenome and population variation data, and aimed to provide a portal for accessing and analyzing pear multiomics data. A variety of online tools were built including gene search, BLAST, JBrowse, expression heatmap, synteny analysis and primer design. The information of DNA methylation sites and single-nucleotide polymorphisms can be retrieved through the custom JBrowse, providing an opportunity to explore the genetic polymorphisms linked to phenotype variation. Moreover, different gene families involving transcription factors, transcription regulators and disease resistance (nucleotide-binding site leucine-rich repeat) were identified and compiled for quick search. In particular, biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) were identified in pear genomes, and specialized webpages were set up to show detailed information of BGCs, laying a foundation for studying metabolic diversity among different pear varieties. Overall, PearMODB provides an important platform for pear genomics, genetics and breeding studies. Database URL http://pearomics.njau.edu.cn.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The pear genomics database (PGDB): a comprehensive multi-omics research platform for Pyrus spp.BMC Plant Biol. 2023 Sep 15;23(1):430. doi: 10.1186/s12870-023-04406-5. BMC Plant Biol. 2023. PMID: 37710163 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide comparative analysis of the BAHD superfamily in seven Rosaceae species and expression analysis in pear (Pyrus bretschneideri).BMC Plant Biol. 2020 Jan 8;20(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-2230-z. BMC Plant Biol. 2020. PMID: 31914928 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of the P-type ATPase gene family in seven Rosaceae species and an expression analysis in pear (Pyrus bretschneideri Rehd.).Genomics. 2020 May;112(3):2550-2563. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2020.02.008. Epub 2020 Feb 10. Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32057915
-
Plant biochemical genetics in the multiomics era.J Exp Bot. 2023 Aug 17;74(15):4293-4307. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erad177. J Exp Bot. 2023. PMID: 37170864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of physics in multiomics and cancer evolution.Front Oncol. 2023 Mar 17;13:1068053. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1068053. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37007140 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Functional characterization of COMT genes in Chinese white pear (Pyrus bretschneideri) and their role in lignin synthesis.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Jun 9;16:1614220. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1614220. eCollection 2025. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 40551766 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of POD genes and their expression under multiple hormones in Pyrus bretschenedri.BMC Genom Data. 2024 May 6;25(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s12863-024-01229-7. BMC Genom Data. 2024. PMID: 38711007 Free PMC article.
-
Exogenous GA3 Enhances Nitrogen Uptake and Metabolism under Low Nitrate Conditions in 'Duli' (Pyrus betulifolia Bunge) Seedlings.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 21;25(14):7967. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147967. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39063209 Free PMC article.
-
Haplotype-resolved T2T genome assemblies and pangenome graph of pear reveal diverse patterns of allele-specific expression and the genomic basis of fruit quality traits.Plant Commun. 2024 Oct 14;5(10):101000. doi: 10.1016/j.xplc.2024.101000. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Plant Commun. 2024. PMID: 38859586 Free PMC article.
-
Primary metabolomics and transcriptomic techniques were used to explore the regulatory mechanisms that may influence the flavor characteristics of fresh Corylus heterophylla × Corylus avellana.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Jan 30;15:1475242. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1475242. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 39949634 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Potter D., Eriksson T., Evans R.C.. et al. (2007) Phylogeny and classification of Rosaceae. Plant Syst. Evol., 266, 5–43.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- BK20210397/Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province
- JBGS(2021)022/seed industry promotion project of Jiangsu
- 2022YFF1003100-02/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions
- JCQY201901/Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities
- CX(22)2025/Jiangsu Agriculture Science and Technology Innovation Fund
- 31830081 32172511/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- NAUSY-MS08/guidance foundation of Hainan Institute of Nanjing Agricultural University
- CARS-28/Earmarked Fund for China Agriculture Research System
- BK20210397/Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province
- JBGS(2021)022/seed industry promotion project of Jiangsu
- 2022YFF1003100-02/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions
- JCQY201901/Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities
- CX(22)2025/Jiangsu Agriculture Science and Technology Innovation Fund
- 31830081 32172511/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- NAUSY-MS08/guidance foundation of Hainan Institute of Nanjing Agricultural University
- CARS-28/Earmarked Fund for China Agriculture Research System
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

