Prognostic value of HER2-low status in breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 37413762
- PMCID: PMC10485402
- DOI: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2023.101592
Prognostic value of HER2-low status in breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-low expression in breast cancer has been recently identified as a new therapeutic target. However, it is unclear if HER2-low status has an independent impact on prognosis.
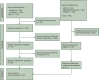
Materials and methods: A systematic literature research was carried out to identify studies comparing survival outcomes of patients affected by HER2-low versus HER2-zero breast cancer. Using random-effects models, pooled hazard ratios (HRs) and odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated for progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in the metastatic setting as well as disease-free survival (DFS), OS and pathological complete response (pCR) in the early setting. Subgroup analyses by hormone receptor (HoR) status were carried out. The study protocol is registered on PROSPERO (n.CRD42023390777).
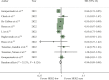
Results: Among 1916 identified records, 42 studies including 1 797 175 patients were eligible. In the early setting, HER2-low status was associated with significant improved DFS (HR 0.86, 95% CI 0.79-0.92, P < 0.001) and OS (HR 0.90, 95% CI 0.85-0.95, P < 0.001) when compared to HER2-zero status. Improved OS was observed for both HoR-positive and HoR-negative HER2-low populations, while DFS improvement was observed only in the HoR-positive subgroup. HER2-low status was significantly associated with a lower rate of pCR as compared to HER2-zero status both in the overall population (OR 0.74, 95% CI 0.62-0.88, P = 0.001) and in the HoR-positive subgroup (OR 0.77, 95% CI 0.65-0.90, P = 0.001). In the metastatic setting, patients with HER2-low breast cancers showed better OS when compared with those with HER2-zero tumours in the overall population (HR 0.94, 95% CI 0.89-0.98, P = 0.008), regardless of HoR status. No significant PFS differences were found.
Conclusions: Compared with HER2-zero status, HER2-low status appears to be associated with a slightly increased OS both in the advanced and early settings, regardless of HoR expression. In the early setting, HER2-low tumours seem to be associated to lower pCR rates, especially if HoR-positive.
Keywords: HER2-low; HER2-zero; breast cancer.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure CM reports support to attend medical conferences from Gilead and honoraria from Novartis and Lilly (all outside the submitted work). EA reports consultancy fees/honoraria from Eli Lilly, Sandoz, AstraZeneca, research grant to her institution from Gilead and support for attending medical conferences from Novartis, Roche, Eli Lilly, Genetic, Istituto Gentili, Daiichi Sankyo, AstraZeneca. GNM reports support to attend medical conferences from Roche and Bayer (all outside the submitted work). AP reports advisory and consulting fees from Roche, Pfizer, Novartis, Amgen, BMS, Puma, Oncolytics Biotech, MSD, Guardant Health, Peptomyc and Lilly, lecture fees from Roche, Pfizer, Novartis, Amgen, BMS, Nanostring Technologies and Daiichi Sankyo, institutional financial interests from Boehringer, Novartis, Roche, Nanostring, Sysmex Europe GmbH, Medica Scientia inno. Re-search, SL, Celgene, Astellas and Pfizer; and shares ownership and a leadership role in Reveal Genomics, SL. EB reports funding to her institution from Gilead Science. FS declares personal fees for educational activities from Novartis and Gilead and travel expenses from Gilead, Novartis and Daiichy Sankyo. GV received honoraria for advisory boards and consulting fees from Roche, AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, MSD Oncology and Pfizer. LDM reports institutional research grant from Eli Lilly, Novartis, Roche, Daiichi Sankyo and Seagen, consulting fees from Eli Lilly; honoraria from Roche, Novartis, Pfizer, Eli Lilly, AstraZeneca, Merck Sharp and Dohme, Seagen, Gilead, Pierre Fabre, Eisa, Exact Sciences and Ipsen and support for attending meetings from Roche, Pfizer and Eisai; and fees for participation on a data safety monitoring board or advisory board from Novartis, Roche, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Daiichi-Sankyo, Exact Sciences, Gilead, Pierre Fabre, Eisai, AstraZeneca and Agendia. ML played an advisory role for Roche, Lilly, Novartis, Astrazeneca, Pfizer, Seagen, Gilead, MSD and Exact Sciences and received speaker honoraria from Roche, Daiichi Sankyo, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Sandoz, Libbs and Takeda and travel grants from Gilead outside the submitted work. EDA received honoraria and/or participated to advisory board from Roche/GNE, Novartis, Seattle Genetics, Zodiac, Libbs and Pierre Fabre; received travel grants from Roche/GNE and GSK/Novartis; and received research grant to his institution from Roche/GNE, AstraZeneca, GSK/Novartis and Servier. All other authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Siegel R.L., Miller K.D., Wagle N.S., Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023;73(1):17–48. - PubMed
-
- Harbeck N., Gnant M. Breast cancer. Lancet. 2017;389(10074):1134–1150. - PubMed
-
- Wolff A.C., Hammond M.E.H., Allison K.H., et al. Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists clinical practice guideline focused update. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(20):2105–2122. - PubMed
-
- Tarantino P., Hamilton E., Tolaney S.M., et al. HER2-low breast cancer: pathological and clinical landscape. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38(17):1951–1962. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

