Humoral immune responses associated with control of SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infections in a vaccinated US military population
- PMID: 37413891
- PMCID: PMC10345251
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2023.104683
Humoral immune responses associated with control of SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infections in a vaccinated US military population
Abstract
Background: COVID-19 vaccines have been critical for protection against severe disease following infection with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) but gaps remain in our understanding of the immune responses that contribute to controlling subclinical and mild infections.
Methods: Vaccinated, active-duty US military service members were enrolled in a non-interventional, minimal-risk, observational study starting in May, 2021. Clinical data, serum, and saliva samples were collected from study participants and were used to characterise the humoral immune responses to vaccination and to assess its impact on clinical and subclinical infections, as well as virologic outcomes of breakthrough infections (BTI) including viral load and infection duration.
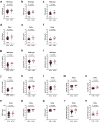
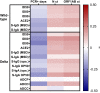
Findings: The majority of VIRAMP participants had received the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine and by January, 2022, N = 149 had a BTI. The median BTI duration (PCR+ days) was 4 days and the interquartile range was 1-8 days. Participants that were nucleocapsid seropositive prior to their BTI had significantly higher levels of binding and functional antibodies to the spike protein, shorter median duration of infections, and lower median peak viral loads compared to seronegative participants. Furthermore, levels of neutralising antibody, ACE2 blocking activity, and spike-specific IgA measured prior to BTI also correlated with the duration of infection.
Interpretation: We extended previous findings and demonstrate that a subset of vaccine-induced humoral immune responses, along with nucleocapsid serostatus are associated with control of SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infections in the upper airways.
Funding: This work was funded by the DoD Joint Program Executive Office for Chemical, Biological, Radiological and Nuclear Defense (JPEO-CBRND) in collaboration with the Defense Health Agency (DHA) COVID-19 funding initiative for the VIRAMP study.
Keywords: Antibody responses; Breakthrough infection duration; COVID-19 vaccine; SARS-CoV-2.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests KM (Allucent) was contracted by the US Department of Defense to conduct the VIRAMP clinical study, to perform testing on clinical study samples, and to collect epidemiologic data. JC served as the Acting Chief Medical Officer for the Vaccine Acceleration Program at the Joint Program Executive Office for Chemical, Biological, Radiological and Nuclear Defense that funded the VIRAMP clinical study, and was involved with clinical study design and establishing collaborations for analysis of samples. The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Khoury D.S., Cromer D., Reynaldi A., et al. Neutralizing antibody levels are highly predictive of immune protection from symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat Med. 2021;27(7):1205–1211. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

