Urine drug testing among Medicaid enrollees initiating buprenorphine treatment for opioid use disorder within 9 MODRN states
- PMID: 37413960
- PMCID: PMC10529442
- DOI: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2023.110875
Urine drug testing among Medicaid enrollees initiating buprenorphine treatment for opioid use disorder within 9 MODRN states
Abstract
Background: Treatment guidelines recommend regular urine drug testing (UDT) for persons initiating buprenorphine for opioid use disorder (OUD). However, little is known about UDT utilization. We describe state variation in UDT utilization and examine demographic, health, and health care utilization factors associated with UDT in Medicaid.
Methods: We used Medicaid claims and enrollment data from persons initiating buprenorphine treatment for OUD during 2016-2019 in 9 states (DE, KY, MD, ME, MI, NC, PA, WI, WV). The main outcome was at least 1 UDT within 180 days of buprenorphine initiation, the secondary outcome was at least 3. Logistic regression models included demographics, pre-initiation comorbidities, and health service use. State estimates were pooled using meta-analysis.
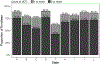
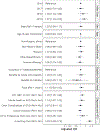
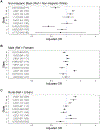
Results: The study cohort included 162,437 Medicaid enrollees initiating buprenorphine. The percent receiving ≥1 UDT varied from 62.1% to 89.8% by state. In the pooled analysis, enrollees with pre-initiation UDT had much higher odds of ≥1 UDT after initiation (aOR=3.83, 3.09-4.73); odds were also higher for enrollees with HIV, HCV, and/or HBV infection (aOR=1.25, 1.05-1.48) or who initiated in later years (2018 v 2016: aOR=1.39, 1.03-1.89; 2019 v 2016: aOR=1.67, 1.24-2.25). The odds of having ≥3 UDT were lower with pre-initiation opioid overdose (aOR=0.79, 0.64-0.96) and higher with pre-initiation UDT (aOR=2.63, 2.13-3.25) or OUD care (aOR=1.35, 1.04-1.74). The direction of associations with demographics varied by state.
Conclusions: Rates of UDT increased over time and there was variability among states in UDT rates and demographic predictors of UDT. Pre-initiation conditions, UDT, and OUD care were associated with UDT.
Keywords: Buprenorphine; Drug testing; Medicaid; Opioid use disorder; Overdose; Urinalysis.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest No conflict declared.
Figures

References
-
- Austin AE, Tang L, Kim JY, Allen L, Barnes AJ, Chang C-CH, Clark S, Cole ES, Durrance CP, Donohue JM, Gordon AJ, Huskamp HA, McDuffie MJ, Mehrotra A, Mohamoud S, Talbert J, Ahrens KA, Applegate M, Hammerslag LR, Lanier P, Tossone K, Zivin K, Burns ME, 2023. Trends in Use of Medication to Treat Opioid Use Disorder During the COVID-19 Pandemic in 10 State Medicaid Programs. JAMA Health Forum 4, e231422. 10.1001/jamahealthforum.2023.1422 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

