Large-scale detection and characterization of interchromosomal rearrangements in normozoospermic bulls using massive genotype and phenotype data sets
- PMID: 37414574
- PMCID: PMC10519396
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.277787.123
Large-scale detection and characterization of interchromosomal rearrangements in normozoospermic bulls using massive genotype and phenotype data sets
Abstract
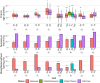
In this paper, we developed a highly sensitive approach to detect interchromosomal rearrangements in cattle by searching for abnormal linkage disequilibrium patterns between markers located on different chromosomes in large paternal half-sib families genotyped as part of routine genomic evaluations. We screened 5571 families of artificial insemination sires from 15 breeds and revealed 13 putative interchromosomal rearrangements, 12 of which were validated by cytogenetic analysis and long-read sequencing. These consisted of one Robertsonian fusion, 10 reciprocal translocations, and the first case of insertional translocation reported in cattle. Taking advantage of the wealth of data available in cattle, we performed a series of complementary analyses to define the exact nature of these rearrangements, investigate their origins, and search for factors that may have favored their occurrence. We also evaluated the risks to the livestock industry and showed significant negative effects on several traits in the sires and in their balanced or aneuploid progeny compared with wild-type controls. Thus, we present the most comprehensive and thorough screen for interchromosomal rearrangements compatible with normal spermatogenesis in livestock species. This approach is readily applicable to any population that benefits from large genotype data sets, and will have direct applications in animal breeding. Finally, it also offers interesting prospects for basic research by allowing the detection of smaller and rarer types of chromosomal rearrangements than GTG banding, which are interesting models for studying gene regulation and the organization of genome structure.
© 2023 Jourdain et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures



References
-
- Achilli F, Bros-Facer V, Williams HP, Banks GT, AlQatari M, Chia R, Tucci V, Groves M, Nickols CD, Seburn KL, et al. 2009. An ENU-induced mutation in mouse glycyl-tRNA synthetase (GARS) causes peripheral sensory and motor phenotypes creating a model of Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 2D peripheral neuropathy. Dis Model Mech 2: 359–373. 10.1242/dmm.002527 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Allais-Bonnet A, Hintermann A, Deloche M-C, Cornette R, Bardou P, Naval-Sanchez M, Pinton A, Haruda A, Grohs C, Zakany J, et al. 2021. Analysis of polycerate mutants reveals the evolutionary co-option of HOXD1 for horn patterning in Bovidae. Mol Biol Evol 38: 2260–2272. 10.1093/molbev/msab021 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Antonellis A, Ellsworth RE, Sambuughin N, Puls I, Abel A, Lee-Lin S-Q, Jordanova A, Kremensky I, Christodoulou K, Middleton LT, et al. 2003. Glycyl tRNA synthetase mutations in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2D and distal spinal muscular atrophy type V. Am J Hum Genet 72: 1293–1299. 10.1086/375039 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Balabanian K, Brotin E, Biajoux V, Bouchet-Delbos L, Lainey E, Fenneteau O, Bonnet D, Fiette L, Emilie D, Bachelerie F. 2012. Proper desensitization of CXCR4 is required for lymphocyte development and peripheral compartmentalization in mice. Blood 119: 5722–5730. 10.1182/blood-2012-01-403378 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
