Mathematical model combined with microdosimetric kinetic model for tumor volume calculation in stereotactic body radiation therapy
- PMID: 37414844
- PMCID: PMC10326039
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-38232-4
Mathematical model combined with microdosimetric kinetic model for tumor volume calculation in stereotactic body radiation therapy
Abstract
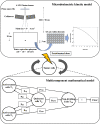
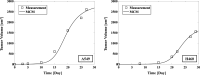
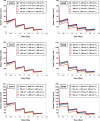
We proposed a new mathematical model that combines an ordinary differential equation (ODE) and microdosimetric kinetic model (MKM) to predict the tumor-cell lethal effect of Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) applied to non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The tumor growth volume was calculated by the ODE in the multi-component mathematical model (MCM) for the cell lines NSCLC A549 and NCI-H460 (H460). The prescription doses 48 Gy/4 fr and 54 Gy/3 fr were used in the SBRT, and the effect of the SBRT on tumor cells was evaluated by the MKM. We also evaluated the effects of (1) linear quadratic model (LQM) and the MKM, (2) varying the ratio of active and quiescent tumors for the total tumor volume, and (3) the length of the dose-delivery time per fractionated dose (tinter) on the initial tumor volume. We used the ratio of the tumor volume at 1 day after the end of irradiation to the tumor volume before irradiation to define the radiation effectiveness value (REV). The combination of MKM and MCM significantly reduced REV at 48 Gy/4 fr compared to the combination of LQM and MCM. The ratio of active tumors and the prolonging of tinter affected the decrease in the REV for A549 and H460 cells. We evaluated the tumor volume considering a large fractionated dose and the dose-delivery time by combining the MKM with a mathematical model of tumor growth using an ODE in lung SBRT for NSCLC A549 and H460 cells.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Assessing tumor volumetric reduction with consideration for setup errors based on mathematical tumor model and microdosimetric kinetic model in single-isocenter VMAT for brain metastases.Phys Eng Sci Med. 2024 Dec;47(4):1385-1396. doi: 10.1007/s13246-024-01451-8. Epub 2024 Jun 17. Phys Eng Sci Med. 2024. PMID: 38884671
-
Local Control After Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Stage I Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021 May 1;110(1):160-171. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.03.045. Epub 2019 Apr 5. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021. PMID: 30954520 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lack of a dose-effect relationship for pulmonary function changes after stereotactic body radiation therapy for early-stage non-small cell lung cancer.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013 Mar 15;85(4):1074-81. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2012.09.016. Epub 2012 Nov 12. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013. PMID: 23154077
-
Assessment of Monte Carlo algorithm for compliance with RTOG 0915 dosimetric criteria in peripheral lung cancer patients treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2016 May 8;17(3):277-293. doi: 10.1120/jacmp.v17i3.6077. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2016. PMID: 27167284 Free PMC article.
-
Organs at Risk Considerations for Thoracic Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy: What Is Safe for Lung Parenchyma?Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021 May 1;110(1):172-187. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2018.11.028. Epub 2018 Nov 26. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021. PMID: 30496880 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Radiobiological Modeling with Monte Carlo Tools - Simulating Cellular Responses to Ionizing Radiation.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2025 Jan-Dec;24:15330338251350909. doi: 10.1177/15330338251350909. Epub 2025 Jul 17. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2025. PMID: 40671567 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mathematical modeling in radiotherapy for cancer: a comprehensive narrative review.Radiat Oncol. 2025 Apr 4;20(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s13014-025-02626-7. Radiat Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40186295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mathematical Modeling Support for Lung Cancer Therapy-A Short Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 25;24(19):14516. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914516. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37833963 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Onishi H, Araki T, Shirato H, Nagata Y, Hiraoka M, Gomi K, et al. Stereotactic hypofractionated high-dose irradiation for stage I nonsmall cell lung carcinoma: Clinical outcomes in 245 subjects in a Japanese multiinstitutional study. Cancer. 2004;101:1623–1631. doi: 10.1002/cncr.20539. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Palma D, Visser O, Lagerwaard FJ, Belderbos J, Slotman BJ, Senan S. Impact of introducing stereotactic lung radiotherapy for elderly patients with stage I non-small cell lung cancer: A population-based time-trend analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010;28:5153–5159. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.30.0731. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Schneider BJ, Daly ME, Kennedy EB, Antonoff MB, Broderick S, Feldman J, et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Endorsement of the American Society for Radiation Oncology Evidence-Based Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018;36(7):710–719. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.74.9671. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

