The emerging roles of SUMOylation in the tumor microenvironment and therapeutic implications
- PMID: 37415251
- PMCID: PMC10324244
- DOI: 10.1186/s40164-023-00420-3
The emerging roles of SUMOylation in the tumor microenvironment and therapeutic implications
Abstract
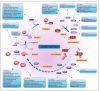
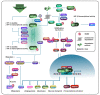
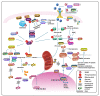
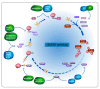
Tumor initiation, progression, and response to therapies depend to a great extent on interactions between malignant cells and the tumor microenvironment (TME), which denotes the cancerous/non-cancerous cells, cytokines, chemokines, and various other factors around tumors. Cancer cells as well as stroma cells can not only obtain adaption to the TME but also sculpt their microenvironment through a series of signaling pathways. The post-translational modification (PTM) of eukaryotic cells by small ubiquitin-related modifier (SUMO) proteins is now recognized as a key flexible pathway. Proteins involved in tumorigenesis guiding several biological processes including chromatin organization, DNA repair, transcription, protein trafficking, and signal conduction rely on SUMOylation. The purpose of this review is to explore the role that SUMOylation plays in the TME formation and reprogramming, emphasize the importance of targeting SUMOylation to intervene in the TME and discuss the potential of SUMOylation inhibitors (SUMOi) in ameliorating tumor prognosis.
Keywords: Clinical implications; Hypoxia; Immune response; Inflammation; Metabolism; Post-translational modification; SUMOylation; Tumor microenvironment.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SUMOylation in Skeletal Development, Homeostasis, and Disease.Cells. 2022 Aug 31;11(17):2710. doi: 10.3390/cells11172710. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36078118 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The post-translational modification, SUMOylation, and cancer (Review).Int J Oncol. 2018 Apr;52(4):1081-1094. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2018.4280. Epub 2018 Feb 22. Int J Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29484374 Free PMC article. Review.
-
E2-mediated small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) modification of thymine DNA glycosylase is efficient but not selective for the enzyme-product complex.J Biol Chem. 2014 May 30;289(22):15810-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.572081. Epub 2014 Apr 21. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24753249 Free PMC article.
-
SUMOylation Pattern Predicts Prognosis and Indicates Tumor Microenvironment Infiltration Characterization in Bladder Cancer.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 28;13:864156. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.864156. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35418978 Free PMC article.
-
Sumoylation in Physiology, Pathology and Therapy.Cells. 2022 Feb 26;11(5):814. doi: 10.3390/cells11050814. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35269436 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multi-omics dissection of tumor microenvironment-mediated drug resistance: mechanisms and therapeutic reprogramming.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jul 7;16:1634413. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1634413. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40693266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Post-Translational Modifications of RNA-Modifying Proteins in Cellular Dynamics and Disease Progression.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Nov;11(44):e2406318. doi: 10.1002/advs.202406318. Epub 2024 Oct 8. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 39377984 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PIAS family in cancer: from basic mechanisms to clinical applications.Front Oncol. 2024 Mar 25;14:1376633. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1376633. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38590645 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Implications of the SUMOylation Pathway in Acute Myeloid Leukemia.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Feb 13;17(4):631. doi: 10.3390/cancers17040631. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40002226 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive antitumor immune response boosted by dual inhibition of SUMOylation and MEK in MYC-expressing KRAS-mutant cancers.Exp Hematol Oncol. 2024 Sep 27;13(1):94. doi: 10.1186/s40164-024-00563-x. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39334463 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu J, Qian C, Cao X. Post-Translational Modif Control Innate Immun Immun. 2016;45(1):15–30. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
- 82173347/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82173347/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82173347/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82173347/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82173347/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82173347/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82173347/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82173347/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82173347/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- JX10231801/Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions
- JX10231801/Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions
- JX10231801/Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions
- JX10231801/Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions
- JX10231801/Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions
- JX10231801/Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions
- JX10231801/Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions
- JX10231801/Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions
- JX10231801/Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

