The COVID-19 pandemic and healthcare utilization in Iran: evidence from an interrupted time series analysis
- PMID: 37415435
- PMCID: PMC10522821
- DOI: 10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0041
The COVID-19 pandemic and healthcare utilization in Iran: evidence from an interrupted time series analysis
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to examine the effect of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak on the hospitalization rate, emergency department (ED) visits, and outpatient clinic visits in western Iran.
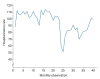
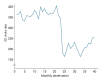
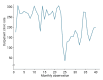
Methods: We collected data on the monthly hospitalization rate, rate of patients referred to the ED, and rate of patients referred to outpatient clinics for a period of 40 months (23 months before and 17 months after the COVID-19 outbreak in Iran) from all 7 public hospitals in the city of Kermanshah. An interrupted time series analysis was conducted to examine the impact of COVID-19 on the outcome variables in this study.
Results: A statistically significant decrease of 38.11 hospitalizations per 10,000 population (95% confidence interval [CI], 24.93-51.29) was observed in the first month of the COVID-19 outbreak. The corresponding reductions in ED visits and outpatient visits per 10,000 population were 191.65 (95% CI, 166.63-216.66) and 168.57 (95% CI, 126.41-210.73), respectively. After the initial reduction, significant monthly increases in the hospitalization rate (an increase of 1.81 per 10,000 population), ED visits (an increase of 2.16 per 10,000 population), and outpatient clinic visits (an increase of 5.77 per 10,000 population) were observed during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Conclusion: Our study showed that the utilization of outpatient and inpatient services in hospitals and clinics significantly declined after the COVID-19 outbreak, and use of these services did not return to pre-outbreak levels as of June 2021.
Keywords: COVID-19; Hospital outpatient clinic; Iran; Patient care.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The impact of COVID-19 pandemic on hospital admissions for nine diseases in Iran: insight from an interrupted time series analysis.Cost Eff Resour Alloc. 2022 Nov 1;20(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s12962-022-00394-9. Cost Eff Resour Alloc. 2022. PMID: 36319966 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on governmental hospitals performance indicators in city of Yazd, Iran: an interrupted time-series analysis.BMC Health Serv Res. 2025 Mar 26;25(1):438. doi: 10.1186/s12913-025-12587-y. BMC Health Serv Res. 2025. PMID: 40140858 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on health services utilization in China: Time-series analyses for 2016-2020.Lancet Reg Health West Pac. 2021 Mar 24;9:100122. doi: 10.1016/j.lanwpc.2021.100122. eCollection 2021 Apr. Lancet Reg Health West Pac. 2021. PMID: 34327438 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of the Covid-19 pandemic on outpatient visits for patients with cancer in Iran: an interrupted time series analysis.Arch Public Health. 2025 Jan 6;83(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s13690-024-01482-3. Arch Public Health. 2025. PMID: 39757223 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 Pandemic and Hospital Efficiency in Iran: Insight from an Interrupted Time Series Analysis and Pabon Lasso Model.J Lifestyle Med. 2022 Sep 30;12(3):178-187. doi: 10.15280/jlm.2022.12.3.178. J Lifestyle Med. 2022. PMID: 36628180 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The strongest predictors of compliance with health protocols among marketers and guilds based on the transtheoretical model.BMC Public Health. 2024 Jul 15;24(1):1892. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-19386-w. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39010015 Free PMC article.
-
Time series analysis of COVID-19's impact on physician and dentist visits in Iran.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 16;14(1):16453. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-67238-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39013932 Free PMC article.
-
Changes and backlogs in the provision and utilization of essential health services in Afghanistan during and after the COVID-19 pandemic.BMC Health Serv Res. 2025 Jul 3;25(1):923. doi: 10.1186/s12913-025-13093-x. BMC Health Serv Res. 2025. PMID: 40611256 Free PMC article.
-
A tale of two times: an exploration of healthcare utilization patterns before and during COVID-19 in Iran.BMC Public Health. 2024 Oct 25;24(1):2961. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-20452-6. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39455941 Free PMC article.
-
From Routine to Crisis: The Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Antibiotic Consumption in Iran.Health Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 29;7(11):e70161. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.70161. eCollection 2024 Nov. Health Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39474349 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grasselli G, Pesenti A, Cecconi M. Critical care utilization for the COVID-19 outbreak in Lombardy, Italy: early experience and forecast during an emergency response. JAMA. 2020;323:1545–6. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

