Early low blood MALT1 expression levels forecast better efficacy of PD‑1 inhibitor‑based treatment in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer
- PMID: 37415633
- PMCID: PMC10320427
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2023.13915
Early low blood MALT1 expression levels forecast better efficacy of PD‑1 inhibitor‑based treatment in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer
Abstract
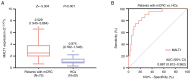
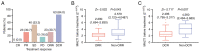
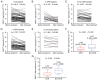
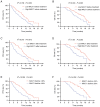
Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation protein 1 (MALT1) modulates colorectal cancer (CRC) malignant behaviors and tumor immune escape. The present study aimed to explore the association of MALT1 with treatment response and survival time among patients with metastatic CRC (mCRC) after programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1) inhibitor-based treatment. MALT1 from the blood samples of 75 patients with unresectable mCRC receiving PD-1 inhibitor-based treatment at baseline and after 2-cycle treatment, as well as 20 healthy controls (HCs), was detected by reverse transcription-quantitative PCR. In the patients with mCRC, the objective response rate (ORR), disease control rate (DCR), progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were calculated. MALT1 expression was elevated in patients with mCRC compared with that in HCs (P<0.001). In patients with mCRC, MALT1 expression was positively correlated with multiple (vs. single) metastasis (P=0.032) and peritoneum metastasis (P=0.029). MALT1 levels before treatment were decreased in ORR patients vs. non-ORR patients (P=0.043) and in DCR patients vs. non-DCR patients (P=0.007). Additionally, MALT1 expression was reduced after treatment compared with that before treatment (P<0.001). Meanwhile, MALT1 expression after treatment was notably decreased in ORR patients vs. non-ORR patients (P<0.001) and in DCR patients vs. non-DCR patients (P<0.001). Furthermore, a low MALT1 level before treatment was associated with longer PFS (P=0.030) and OS (P=0.025) times. Decreased MALT1 expression after treatment and a decline in MALT1 expression of >30% after treatment (ratio to MALT1 before treatment) (both P≤0.001) presented more significant associations with prolonged PFS and OS times. In conclusion, early low levels of blood MALT1 during therapy may predict an improved response to PD-1 inhibitor-based treatment and survival time in patients with mCRC.
Keywords: MALT1; PD-1 inhibitor; mCRC; survival; treatment response.
Copyright: © Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Changes in mucosa‑associated lymphoid tissue 1 predicts therapeutic response and survival in patients with advanced melanoma receiving programmed cell death‑1 inhibitor monotherapy.Oncol Lett. 2024 Jul 12;28(3):433. doi: 10.3892/ol.2024.14566. eCollection 2024 Sep. Oncol Lett. 2024. PMID: 39049986 Free PMC article.
-
Blood MALT1 serves as a potential biomarker reflecting the response and survival of immune‑checkpoint‑inhibitor therapy in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncol Lett. 2024 Aug 5;28(4):476. doi: 10.3892/ol.2024.14609. eCollection 2024 Oct. Oncol Lett. 2024. PMID: 39161329 Free PMC article.
-
Vertical level of blood cell division cycle 42 predicts response and survival benefits to PD-1 inhibitor-based regimen in metastatic colorectal cancer patients.Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2023 Apr;83(2):103-110. doi: 10.1080/00365513.2023.2175330. Epub 2023 Feb 22. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2023. PMID: 36811410
-
Surrogate endpoints in second-line treatment for mCRC: a systematic literature-based analysis from 23 randomised trials.Acta Oncol. 2015 Feb;54(2):187-93. doi: 10.3109/0284186X.2014.938830. Epub 2014 Jul 14. Acta Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25017379 Review.
-
Chemotherapeutic Effectiveness of Combining Cetuximab for Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Treatment: A System Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Oncol. 2020 May 28;10:868. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00868. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32547954 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Changes in mucosa‑associated lymphoid tissue 1 predicts therapeutic response and survival in patients with advanced melanoma receiving programmed cell death‑1 inhibitor monotherapy.Oncol Lett. 2024 Jul 12;28(3):433. doi: 10.3892/ol.2024.14566. eCollection 2024 Sep. Oncol Lett. 2024. PMID: 39049986 Free PMC article.
-
Blood MALT1 expression levels reflect the lymph node stage and disease-free survival in patients with non-small cell lung cancer.Oncol Lett. 2025 Jun 3;30(2):381. doi: 10.3892/ol.2025.15127. eCollection 2025 Aug. Oncol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40503039 Free PMC article.
References
-
- You YN, Hardiman KM, Bafford A, Poylin V, Francone TD, Davis K, Paquette IM, Steele SR, Feingold DL. On Behalf of the Clinical Practice Guidelines Committee of the American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons: The American Society of Colon and rectal surgeons clinical practice guidelines for the management of rectal cancer. Dis Colon Rectum. 2020;63:1191–1222. doi: 10.1097/DCR.0000000000001762. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
