Association between diabetes status and breast cancer in US adults: findings from the US National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- PMID: 37415670
- PMCID: PMC10321597
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1059303
Association between diabetes status and breast cancer in US adults: findings from the US National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Abstract
Objectives: The aim of this study was to investigate the association between diabetes status and the risk of breast cancer among adult Americans, exploring the impact of BMI, age, and race on this relationship.
Methods: A cross-sectional analysis of 8,249 individuals from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) was conducted. Diabetes was categorized as type 2 diabetes and prediabetes, with both conditions diagnosed according to the ADA 2014 guidelines. The association between diabetes status and breast cancer risk was explored using multiple logistic regression analysis.
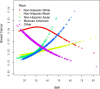
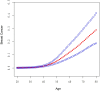
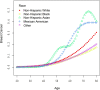
Results: Patients with diabetes had higher odds of breast cancer (OR: 1.51; 95% CI 1.00 to 2.28), Using the two-piecewise linear regression model, it was observed that there is a threshold effect in the risk of breast cancer occurrence at the age of 52 years. Specifically, the risk of breast cancer is relatively low before the age of 52 but increases significantly after this age.
Conclusions: This study identified a significant association between diabetes status and breast cancer risk among adult Americans. We also found a threshold effect in breast cancer occurrence at the age of 52. Age was significantly associated with breast cancer risk in both Non-Hispanic White and Non-Hispanic Black individuals. These findings underscore the importance of diabetes management, maintaining a healthy BMI, and age-related risk considerations in reducing breast cancer risk.
Keywords: NHANES; breast cancer; diabetes status; obesity; prediabetes; type 2 diabetes.
Copyright © 2023 Sun, Zhang, Kadier, Hu, Liu, Liu, Yan, Sun, Yau, Lowe, Meng, Liu and Zhou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
National patterns in diabetes screening: data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2005-2012.J Gen Intern Med. 2015 May;30(5):612-8. doi: 10.1007/s11606-014-3147-8. Epub 2014 Dec 23. J Gen Intern Med. 2015. PMID: 25533392 Free PMC article.
-
The Association of Prediabetes and Diabetes Risk Perception With Leisure-Time Physical Activity and Weight Loss.Am J Health Promot. 2019 May;33(4):534-540. doi: 10.1177/0890117118803107. Epub 2018 Oct 1. Am J Health Promot. 2019. PMID: 30270634
-
Consistent ethnic specific differences in diabetes risk and vitamin D status in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2016 Nov;164:4-10. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2015.09.023. Epub 2015 Sep 16. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26386461
-
Reach and Use of Diabetes Prevention Services in the United States, 2016-2017.JAMA Netw Open. 2019 May 3;2(5):e193160. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.3160. JAMA Netw Open. 2019. PMID: 31074808 Free PMC article.
-
Adult BMI change and risk of Breast Cancer: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2005-2010.Breast Cancer. 2015 Nov;22(6):648-56. doi: 10.1007/s12282-015-0638-3. Epub 2015 Sep 8. Breast Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26350490 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Associations between surrogate insulin resistance indexes and osteoarthritis: NHANES 2003-2016.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 10;15(1):1578. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-84317-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39794440 Free PMC article.
-
Association between diabetes and subsequent malignancy risk among older breast cancer survivors.JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2024 Apr 30;8(3):pkae036. doi: 10.1093/jncics/pkae036. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38718185 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic Potential of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and Radiotherapy in Breast Cancer Treatment: A New Therapeutic Avenue (TROD-GROG 006).Curr Radiopharm. 2025;18(4):318-332. doi: 10.2174/0118744710381356250429045716. Curr Radiopharm. 2025. PMID: 40329735
-
A burden of proof study of the effects of exposure to high fasting plasma glucose on the risk of seven types of cancer.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 7;15(1):28859. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-13045-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40775253 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetes Mellitus and Thyroid Cancers: Risky Correlation, Underlying Mechanisms and Clinical Prevention.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024 Feb 16;17:809-823. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S450321. eCollection 2024. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024. PMID: 38380275 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Cancer Research Fund . Breast cancer statistics . World Cancer Research Research Fund International. Available at: https://www.wcrf.org/dietandcancer/cancer-trends/breast-cancer-statistics (Accessed August 17, 2020).
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Breast cancer statistics . Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/breast/statistics/index.htm (Accessed August 17, 2020).
-
- The American Cancer Society medical and editorial content team . About breast cancer (2020). AmericanCancerSociety,Inc. Available at: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/breast-cancer/about/how-common-is-breast-c... (Accessed August 17, 2020).
-
- Paths to prevention the California breast cancer primary prevention plan . Available at: https://escholarship.org/uc/item/1v2745z0 (Accessed 1 December 2020).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

