Myopia in elementary school students in Eastern China during the COVID-19 pandemic
- PMID: 37415713
- PMCID: PMC10320216
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1167379
Myopia in elementary school students in Eastern China during the COVID-19 pandemic
Abstract
Background: Myopia is an increasingly serious public concern, particularly among primary school students. The prevalence of myopia and its influencing factors in primary school pupils in Eastern China during the COVID-19 pandemic had not been explored.
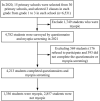
Methods: A randomly clustered sampling method was performed, and selected pupils from grade 1 to grade 3 in 15 primary schools in the Fenghua District of Zhejiang Province were included and given myopia screening and uniform questionnaire survey 1 year later.
Results: A total of 4,213 students completed the myopia screening and questionnaire survey. Myopia was diagnosed in 1,356 pupils, with a myopia incidence of 32.19%. The spherical equivalent (SE) refraction of the included pupils decreased on average by 0.50 ± 2.15 D 1 year later. The myopia rate was positively correlated with the increase of grade, in which the myopia rate among grade 3 students was the highest at 39.69%. The myopia rate among female students was higher than that among male students. Students residing in urban areas had a higher myopia rate than in rural areas. Maintaining an near work distance ≥33 cm was a significant protective factor (OR = 0.84, 95% CI: 0.74-0.96). Students with two myopic parents had a higher risk of myopia (OR = 1.61, 95% CI: 1.34-1.92).
Conclusion: During the COVID-19 pandemic, the myopia rate among early primary school students in Eastern China was high. More attention and implementation of interventions from health and education departments, such as training the development of good eye behavior, should be considered to strengthen the intervention of myopia in primary school students.
Keywords: COVID-19; influencing factor; myopia; primary school; pupil.
Copyright © 2023 Huang, Shen, Zhou, Gong, Liu, Feng and Cen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Prevalence and Progression of Myopia in Elementary School Students in Shanxi Province, China During the COVID-19 Pandemic.Semin Ophthalmol. 2022 Aug;37(6):756-766. doi: 10.1080/08820538.2022.2087474. Epub 2022 Jun 13. Semin Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35695548
-
Prevalence of myopia among senior students in Fenghua, Eastern China, before and during the COVID-19 pandemic.Front Public Health. 2023 Jun 6;11:1180800. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1180800. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37346105 Free PMC article.
-
Near Work Related Behaviors Associated with Myopic Shifts among Primary School Students in the Jiading District of Shanghai: A School-Based One-Year Cohort Study.PLoS One. 2016 May 3;11(5):e0154671. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0154671. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27139017 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the prevalence of myopia and its associated factors in China: a systemic review.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2023 Sep;27(17):7997-8003. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202309_33559. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37750628
-
Pediatric Myopia Progression During the COVID-19 Pandemic Home Quarantine and the Risk Factors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Public Health. 2022 Jul 22;10:835449. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.835449. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35937221 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Complications of high myopia: An update from clinical manifestations to underlying mechanisms.Adv Ophthalmol Pract Res. 2024 Jun 21;4(3):156-163. doi: 10.1016/j.aopr.2024.06.003. eCollection 2024 Aug-Sep. Adv Ophthalmol Pract Res. 2024. PMID: 39036706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A water transfer printing method for contact lenses surface 2D MXene modification to resist bacterial infection and inflammation.Sci Adv. 2024 Apr 12;10(15):eadl3262. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adl3262. Epub 2024 Apr 10. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 38598619 Free PMC article.
-
The prevalence of myopia and eye health behaviors among 3 to 18 years: a cross-sectional survey study.BMC Public Health. 2025 May 7;25(1):1688. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-22906-x. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40336056 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical