Tumor neoantigens: Novel strategies for application of cancer immunotherapy
- PMID: 37415744
- PMCID: PMC10319592
- DOI: 10.32604/or.2023.029924
Tumor neoantigens: Novel strategies for application of cancer immunotherapy
Abstract
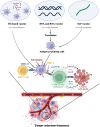
Neoantigen-targeted immunotherapy is a rapidly advancing field that holds great promise for treating cancer. The recognition of antigens by immune cells is a crucial step in tumor-specific killing, and neoantigens generated by mutations in cancer cells possess high immunogenicity and are selectively expressed in tumor cells, making them an attractive therapeutic target. Currently, neoantigens find utility in various domains, primarily in the realm of neoantigen vaccines such as DC vaccines, nucleic acid vaccines, and synthetic long peptide vaccines. Additionally, they hold promise in adoptive cell therapy, encompassing tumor-infiltrating cells, T cell receptors, and chimeric antigen receptors which are expressed by genetically modified T cells. In this review, we summarized recent progress in the clinical use of tumor vaccines and adoptive cell therapy targeting neoantigens, discussed the potential of neoantigen burden as an immune checkpoint in clinical settings. With the aid of state-of-the-art sequencing and bioinformatics technologies, together with significant advancements in artificial intelligence, we anticipated that neoantigens will be fully exploited for personalized tumor immunotherapy, from screening to clinical application.
Keywords: Adoptive T cell therapy; Chimeric antigen receptor; Immunotherapy; Tumor vaccine.
© 2023 Guan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to report regarding the present study.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
