Mechanisms of lung damage in tuberculosis: implications for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- PMID: 37415827
- PMCID: PMC10320222
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1146571
Mechanisms of lung damage in tuberculosis: implications for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Abstract
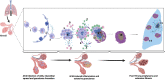
Pulmonary tuberculosis is increasingly recognized as a risk factor for COPD. Severe lung function impairment has been reported in post-TB patients. Despite increasing evidence to support the association between TB and COPD, only a few studies describe the immunological basis of COPD among TB patients following successful treatment completion. In this review, we draw on well-elaborated Mycobacterium tuberculosis-induced immune mechanisms in the lungs to highlight shared mechanisms for COPD pathogenesis in the setting of tuberculosis disease. We further examine how such mechanisms could be exploited to guide COPD therapeutics.
Keywords: COPD - chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; Tuberculosis; adaptive immunity; host-directed therapy (HDT); innate immunity.
Copyright © 2023 Kayongo, Nyiro, Siddharthan, Kirenga, Checkley, Lutaakome Joloba, Ellner and Salgame.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Abadie V., Badell E., Douillard P., Ensergueix D., Leenen P. J., Tanguy M., et al. . (2005). Neutrophils rapidly migrate via lymphatics after mycobacterium bovis BCG intradermal vaccination and shuttle live bacilli to the draining lymph nodes. Blood 106 (5), 1843–1850. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-03-1281 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Abbas A. K., Lichtman A. H., Pillai S. (2019). Basic immunology e-book: functions and disorders of the immune system (Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier Health Sciences; ).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

