Enhanced activity of Ellagic acid in lipid nanoparticles (EA-liposomes) against Acinetobacter baumannii in immunosuppressed mice
- PMID: 37415860
- PMCID: PMC10319833
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2023.103707
Enhanced activity of Ellagic acid in lipid nanoparticles (EA-liposomes) against Acinetobacter baumannii in immunosuppressed mice
Abstract
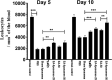
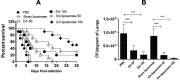
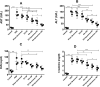
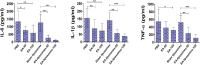
Acinetobacter baumannii infections have come to the surface in huge numbers in the recent decades. Furthermore, A. baumannii has adopted great ability to nullify the majority of currently available antibiotics. With the purpose of finding a nontoxic and efficient therapeutic agent, we analyzed the activity of Ellagic acid (EA) against the multidrug-resistant A. baumannii. EA not only demonstrated its activity against A. baumannii, but also inhibited the biofilm formation. Since EA shows poor solubility in an aqueous environment, a lipid nanoparticle-based (liposomal) formulation of EA (EA-liposomes) was prepared and its effectiveness was assessed to treat bacterial infection in the immunocompromised murine model. Therapy with EA-liposomes imparted greater protection to infected mice by increasing the survival and decreasing the bacterial load in the lungs. A. baumannii infected mice treated with EA-liposomes (100 mg/kg) showed 60% survival rate as compared to 20% of those treated with free EA at the same dose. The bacterial load was found to be 32778 ± 12232 in the lungs of EA-liposomes (100 mg/kg)-treated mice, which was significantly lower to 165667 ± 53048 in the lung tissues of free EA treated mice. Likewise, EA-liposomes also restored the liver function (AST and ALT) and kidney function parameters (BUN and creatinine). The broncho-alveolar fluid (BALF) from infected mice contained greater quantities of IL-6, IL-1β and TNF-α, which were significantly alleviated in EA-liposomes treated mice. These findings together support the possible implication of EA-liposomes to treat A. baumannii infection, especially in immunocompromised mice.
Keywords: Acinetobacter baumannii; Ellagic acid; Immune-suppression; Liposomes.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Liposomal Ellagic Acid Alleviates Cyclophosphamide-Induced Toxicity and Eliminates the Systemic Cryptococcus neoformans Infection in Leukopenic Mice.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Jun 15;13(6):882. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13060882. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34203688 Free PMC article.
-
Glycosphingolipids (GSLs) from Sphingomonas paucimobilis Increase the Efficacy of Liposome-Based Nanovaccine against Acinetobacter baumannii-Associated Pneumonia in Immunocompetent and Immunocompromised Mice.Molecules. 2022 Nov 12;27(22):7790. doi: 10.3390/molecules27227790. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36431892 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial, Immunomodulatory and Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Liposomal Thymoquinone: Implications in the Treatment of Bacterial Pneumonia in Immunocompromised Mice.Biomedicines. 2021 Nov 12;9(11):1673. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9111673. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34829902 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and Therapeutic Efficacy of Thymoquinone-Loaded Liposomes against Drug-Sensitive and Drug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii.Pharmaceutics. 2021 May 8;13(5):677. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13050677. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34066874 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and Prophylactic Efficacy of Liposome-Based Vaccine against the Drug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in Mice.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Jun 27;14(7):1357. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14071357. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35890253 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Anti-microbial, anti-biofilm, and efflux pump inhibitory effects of ellagic acid-bonded magnetic nanoparticles against Escherichia coli isolates.Int Microbiol. 2025 Mar;28(3):563-573. doi: 10.1007/s10123-024-00560-4. Epub 2024 Aug 6. Int Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39105888
-
Nanotechnology Meets Phytotherapy: A Cutting-Edge Approach to Treat Bacterial Infections.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 31;26(3):1254. doi: 10.3390/ijms26031254. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39941020 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanistic Insights into the Biological Effects and Antioxidant Activity of Walnut (Juglans regia L.) Ellagitannins: A Systematic Review.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Aug 10;13(8):974. doi: 10.3390/antiox13080974. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39199220 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigating the anti-growth, anti-resistance, and anti-virulence activities of Schoepfia schreberi J.F.Gmel. against the superbug Acinetobacter baumannii.Heliyon. 2024 May 16;10(10):e31420. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31420. eCollection 2024 May 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38813144 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactive Compounds from Plant Origin as Natural Antimicrobial Agents for the Treatment of Wound Infections.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 8;25(4):2100. doi: 10.3390/ijms25042100. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38396777 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alav I., Sutton J.M., Rahman K.M. Role of bacterial efflux pumps in biofilm formation. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018;73:2003–2020. - PubMed
-
- Alfei S., Turrini F., Catena S., Zunin P., Zuccari G., Pittaluga A.M. Preparation of ellagic acid micro and nano formulations with amazingly increased water solubility 40 by its entrapment in pectin or non-PAMAM dendrimers suitable for clinical applications. New J. Chem. 2019;43:2438–2448.
-
- Alhakamy N.A., Ahmed O.A.A., Kurakula M., Caruso G., Caraci F., Asfour H.Z., Alfarsi A., Eid B.G., Mohamed A.I., Alruwaili N.K., Abdulaal W.H., Fahmy U.A., Alhadrami H.A., Eldakhakhny B.M., Abdel-Naim A.B. Chitosan-Based Microparticles Enhance Ellagic Acid's Colon Targeting and Proapoptotic Activity. Pharmaceutics. 2020;12:652. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Allemailem K.S., Almatroudi A., Alrumaihi F., Aljaghwani A., Alnuqaydan A.M., Khalilullah H., Younus H., El-Kady A.M., Aldakheel F.M., Khan A.A., Khan A., Khan M.A. Antimicrobial, Immunomodulatory and Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Liposomal Thymoquinone: Implications in the Treatment of Bacterial Pneumonia in Immunocompromised Mice. Biomedicines. 2021;9:1673. - PMC - PubMed
Further Reading
-
- Alves M.M.M., Brito L.M., Souza A.C., Queiroz B.C.S.H., de Carvalho T.P., Batista J.F., Oliveira J.S.S.M., de Mendonça I.L., Lira S.R.S., Chaves M.H., Gonçalves J.C.R., Carneiro S.M.P., Arcanjo D.D.R., Carvalho F.A.A. Gallic and ellagic acids: two natural immunomodulator compounds solve infection of macrophages by Leishmania major. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2017;390:893–903. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

