Down-regulation of the Smad signaling by circZBTB46 via the Smad2-PDLIM5 axis to inhibit type I collagen expression
- PMID: 37416515
- PMCID: PMC10320774
- DOI: 10.26599/1671-5411.2023.06.002
Down-regulation of the Smad signaling by circZBTB46 via the Smad2-PDLIM5 axis to inhibit type I collagen expression
Abstract
Background: Abnormal type I collagen (COL1) expression is associated with the development of many cardiovascular diseases. The TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathway and circRNAs have been shown to regulate COL1 gene expression, but the underlying molecular mechanisms are still not fully understood.
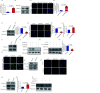
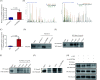
Methods: Gain- and loss-of-function experiments were prformed to study the effect of circZBTB46 on the expression of alpha 2 chain of type I collagen (COL1A2). Co-immunoprecipitation assay was performed to observe the interaction between two proteins. RNA immunoprecipitation assay and biotin pull-down assay were performed to observe the interaction of circZBTB46 with PDLIM5.
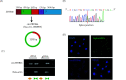
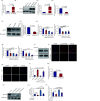
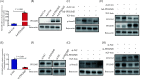
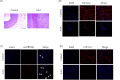
Results: In this study, we investigated the role of circZBTB46 in regulating COL1A2 expression in human vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs). We found that circZBTB46 is expressed in VSMCs and that TGF-beta inhibits circZBTB46 formation by downregulating KLF4 expression through activation of the Smad signaling pathway. CircZBTB46 inhibits the expression of COL1A2 induced by TGF-beta. Mechanistically, circZBTB46 mediates the interaction between Smad2 and PDLIM5, resulting in the inhibition of Smad signaling and the subsequent downregulation of COL1A2 expression. Furthermore, we found that the expression of TGF-beta and COL1A2 is decreased, while circZBTB46 expression is increased in human abdominal aortic aneurysm tissues, indicating that circZBTB46-mediated regulation of TGF-beta/Smad signaling and COL1A2 synthesis in VSMCs plays a crucial role in vascular homeostasis and aneurysm development.
Conclusions: CircZBTB46 was identified as a novel inhibitor of COL1 synthesis in VSMCs, highlighting the importance of circZBTB46 and PDLIM5 in regulating TGF-beta/Smad signaling and COL1A2 expression.
© 2023 JGC All rights reserved; www.jgc301.com.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
