Morphosyntactic development in German-speaking individuals with Down syndrome-longitudinal data
- PMID: 37416537
- PMCID: PMC10321659
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1118659
Morphosyntactic development in German-speaking individuals with Down syndrome-longitudinal data
Abstract
Introduction: The present study provides longitudinal data on the development of receptive and expressive grammar in children and adolescents with Down syndrome and addresses the role of nonverbal cognitive abilities and verbal short-term memory for morphosyntactic development.
Method: Seventeen German-speaking individuals with Down syndrome (aged 4;6-17;1 years at first testing (T1)) were assessed twice, 4;4-6;6 years apart. For a subset of five participants, there was also a third assessment 2 years after the second. Receptive grammar, nonverbal cognition, and verbal short-term memory were tested using standardized measures. For expressive grammar, elicitation tasks were used to assess the production of subject-verb agreement and of wh-questions.
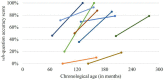
Results: At group level, the participants showed a significant increase in grammar comprehension from T1 to T2. However, progress diminished with increasing chronological age. Notable growth could not be observed beyond the age of 10 years.With respect to expressive grammatical abilities, progress was limited to those participants who had mastered verbal agreement inflection around age 10 years. Individuals who did not master verbal agreement by late childhood achieved no progress in producing wh-questions, either.There was an increase in nonverbal cognitive abilities in the majority of participants. Results for verbal short-term memory followed a similar pattern as those for grammar comprehension. Finally, neither nonverbal cognition nor verbal short-term memory were related to changes in receptive or expressive grammar.
Discussion: The results point to a slowdown in the acquisition of receptive grammar which starts before the teenage years. For expressive grammar, improvement in wh-question production only occurred in individuals with good performance in subject-verb agreement marking, which suggests that the latter might have a trigger function for further grammatical development in German-speaking individuals with Down syndrome. The study provides no indication that nonverbal cognitive abilities or verbal short-term memory performance determined the receptive or expressive development. The results lead to clinical implications for language therapy.
Keywords: Down syndrome; expressive grammar; language development; longitudinal study; receptive grammar; subject-verb agreement; verbal short-term memory; wh-questions.
Copyright © 2023 Witecy, Wimmer, Neitzel and Penke.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Verbal Agreement Inflection in German Children With Down Syndrome.J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2018 Sep 19;61(9):2217-2234. doi: 10.1044/2018_JSLHR-L-17-0241. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2018. PMID: 30458470
-
Language comprehension in children, adolescents, and adults with Down syndrome.Res Dev Disabil. 2017 Mar;62:184-196. doi: 10.1016/j.ridd.2017.01.014. Epub 2017 Feb 7. Res Dev Disabil. 2017. PMID: 28187370
-
Language gains in 4-6-year-old children with developmental language disorder and the relation with language profile, severity, multilingualism and non-verbal cognition.Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2023 May;58(3):765-785. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.12821. Epub 2022 Dec 8. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2023. PMID: 36478026
-
Language and verbal short-term memory skills in children with Down syndrome: a meta-analytic review.Res Dev Disabil. 2011 Nov-Dec;32(6):2225-34. doi: 10.1016/j.ridd.2011.05.014. Epub 2011 May 31. Res Dev Disabil. 2011. PMID: 21628091 Review.
-
Communication interventions for autism spectrum disorder in minimally verbal children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Nov 5;11(11):CD012324. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012324.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30395694 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aktaş M. (2004). Sprachentwicklungsdiagnostik bei Kindern mit Down-Syndrom: Entwicklung eines diagnostischen Leitfadens zum theoriegeleiteten Einsatz standardisierter Verfahren. Bielefeld: Bielefeld University.
-
- Andreou G., Chartomatsidou E. (2020). A review paper on the syntactic abilities of individuals with Down syndrome. Open J. Mod. Linguist. 10, 480–523. doi: 10.4236/ojml.2020.105029 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

