Bidirectional photoswitchability in an iron(iii) spin crossover complex: symmetry-breaking and solvent effects
- PMID: 37416698
- PMCID: PMC10321481
- DOI: 10.1039/d3sc01495a
Bidirectional photoswitchability in an iron(iii) spin crossover complex: symmetry-breaking and solvent effects
Abstract
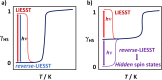
The impact of solvent on spin crossover (SCO) behaviour is reported in two solvates [Fe(qsal-I)2]NO3·2ROH (qsal-I = 4-iodo-2-[(8-quinolylimino)methyl]phenolate; R = Me 1 or Et 2) which undergo abrupt and gradual SCO, respectively. A symmetry-breaking phase transition due to spin-state ordering from a [HS] to [HS-LS] state occurs at 210 K in 1, while T1/2 = 250 K for the EtOH solvate, where complete SCO occurs. The MeOH solvate exhibits LIESST and reverse-LIESST from the [HS-LS] state, revealing a hidden [LS] state. Moreover, photocrystallographic studies on 1 at 10 K reveal re-entrant photoinduced phase transitions to a high symmetry [HS] phase when irradiated at 980 nm or a high symmetry [LS] phase after irradiation at 660 nm. This study represents the first example of bidirectional photoswitchability and subsequent symmetry-breaking from a [HS-LS] state in an iron(iii) SCO material.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures





References
-
- Létard J.-F., Guionneau P. and Goux-Capes L., in Spin Crossover in Transition Metal Compounds III, Springer-Verlag, Berlin/Heidelberg, 2004, pp. 221–249
-
- Senthil Kumar K. Ruben M. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2017;346:176–205. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2017.03.024. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

