VDAC2 malonylation participates in sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction via mitochondrial-related ferroptosis
- PMID: 37416771
- PMCID: PMC10321281
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.84613
VDAC2 malonylation participates in sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction via mitochondrial-related ferroptosis
Abstract
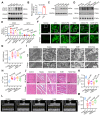
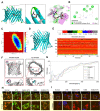
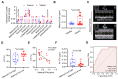
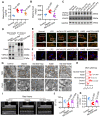
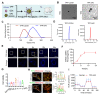
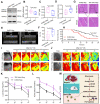
Sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction (SIMD) is a prevalent and severe form of organ dysfunction with elusive underlying mechanisms and limited treatment options. In this study, the cecal ligation and puncture and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) were used to reproduce sepsis model in vitro and vivo. The level of voltage-dependent anion channel 2 (VDAC2) malonylation and myocardial malonyl-CoA were detected by mass spectrometry and LC-MS-based metabolomics. Role of VDAC2 malonylation on cardiomyocytes ferroptosis and treatment effect of mitochondrial targeting nano material TPP-AAV were observed. The results showed that VDAC2 lysine malonylation was significantly elevated after sepsis. In addition, the regulation of VDAC2 lysine 46 (K46) malonylation by K46E and K46Q mutation affected mitochondrial-related ferroptosis and myocardial injury. The molecular dynamic simulation and circular dichroism further demonstrated that VDAC2 malonylation altered the N-terminus structure of the VDAC2 channel, causing mitochondrial dysfunction, increasing mitochondrial ROS levels, and leading to ferroptosis. Malonyl-CoA was identified as the primary inducer of VDAC2 malonylation. Furthermore, the inhibition of malonyl-CoA using ND-630 or ACC2 knock-down significantly reduced the malonylation of VDAC2, decreased the occurrence of ferroptosis in cardiomyocytes, and alleviated SIMD. The study also found that the inhibition of VDAC2 malonylation by synthesizing mitochondria targeting nano material TPP-AAV could further alleviate ferroptosis and myocardial dysfunction following sepsis. In summary, our findings indicated that VDAC2 malonylation plays a crucial role in SIMD and that targeting VDAC2 malonylation could be a potential treatment strategy for SIMD.
Keywords: Ferroptosis; Malonyl-CoA; Malonylation; Sepsis; VDAC2.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Protective Effects of Dexmedetomidine on Sepsis-Induced Vascular Leakage by Alleviating Ferroptosis via Regulating Metabolic Reprogramming.J Inflamm Res. 2021 Dec 10;14:6765-6782. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S340420. eCollection 2021. J Inflamm Res. 2021. PMID: 34916824 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membrane (MAM) regulates steroidogenic activity via steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR)-voltage-dependent anion channel 2 (VDAC2) interaction.J Biol Chem. 2015 Jan 30;290(5):2604-16. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.605808. Epub 2014 Dec 10. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25505173 Free PMC article.
-
Dibutyl phthalate exposure induced mitochondria-dependent ferroptosis by enhancing VDAC2 in zebrafish ZF4 cells.Environ Pollut. 2024 May 1;348:123846. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2024.123846. Epub 2024 Mar 26. Environ Pollut. 2024. PMID: 38548160
-
Sepsis-Induced Myocardial Dysfunction (SIMD): the Pathophysiological Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies Targeting Mitochondria.Inflammation. 2020 Aug;43(4):1184-1200. doi: 10.1007/s10753-020-01233-w. Inflammation. 2020. PMID: 32333359 Review.
-
VDAC2-specific cellular functions and the underlying structure.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Oct;1863(10):2503-14. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2016.04.020. Epub 2016 Apr 23. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 27116927 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sirt5 regulates chondrocyte metabolism and osteoarthritis development through protein lysine malonylation.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 6:2024.07.23.604872. doi: 10.1101/2024.07.23.604872. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025 Apr 2. doi: 10.1002/art.43164. PMID: 39091806 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Development of macrophage-associated genes prognostic signature predicts clinical outcome and immune infiltration for sepsis.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 23;14(1):2026. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-51536-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38263335 Free PMC article.
-
Post-translational acylation of proteins in cardiac hypertrophy.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2025 Apr 14. doi: 10.1038/s41569-025-01150-1. Online ahead of print. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2025. PMID: 40229510 Review.
-
TRIM8 promotes ovarian cancer proliferation and migration by targeting VDAC2 for ubiquitination and degradation.Cancer Med. 2024 Jun;13(11):e7396. doi: 10.1002/cam4.7396. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 38881325 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering Ferroptosis: From Molecular Pathways to Machine Learning-Guided Therapeutic Innovation.Mol Biotechnol. 2025 Apr;67(4):1290-1309. doi: 10.1007/s12033-024-01139-0. Epub 2024 Apr 13. Mol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 38613722 Review.
References
-
- Hollenberg SM, Singer M. Pathophysiology of sepsis- induced cardiomyopathy. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2021;18:424–434. - PubMed
-
- Deng F, Chen Y, Sun QS, Lin ZB, Min Y, Zhao BC. et al. Gut microbiota dysbiosis is associated with sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy in patients: A case-control study. J Med Virol. 2023;95:e28267. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

