Natural History of Chronic Intestinal Pseudo-obstruction and Need for Palliative Care
- PMID: 37417265
- PMCID: PMC10334206
- DOI: 10.5056/jnm22152
Natural History of Chronic Intestinal Pseudo-obstruction and Need for Palliative Care
Abstract
Background/aims: Natural history of chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction (CIPO), a rare disease characterized by episodes of non-mechanical obstruction, is unclear in adults. This study evaluates the clinical course of CIPO and palliative care needs of patients.
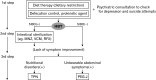
Methods: From October 2010 to September 2021, 74 patients who underwent cine MRI and had a definitive diagnosis of CIPO were prospectively included. We investigated disease etiology and outcomes, age at onset, nutritional status at consultation (body mass index and serum albumin), hydrogen breath test results, and total parenteral nutrition (TPN) during the disease course.
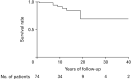
Results: Forty-seven patients (64%) were women, with a mean age of 44 years at onset and 49 years at diagnosis. Primary CIPO was observed in 48 patients (65%). Secondary CIPO was observed in 26 cases (35%), of whom 18 (69%) had scleroderma. The mean body mass index, serum albumin level, and hydrogen breath test positivity rate were 17 kg/m2, 3.8 mg/dL, and 60%, respectively. TPN and invasive decompression therapy were required by 23 (31%) and 18 (24%) patients, respectively. Intestinal sterilization was performed in 51 (69%) patients and was effective in 33 (65%); of these, 28 (85%) were taking metronidazole. Seven (9%) patients used opioids. There were 9 deaths (12%), including 5 (56%) from infection and 2 (22%) from suicide. Of the deaths, 6 (67%) and 4 (44%) underwent TPN management and decompression therapy, respectively. Fifty-one patients (69%) wanted palliative care.
Conclusion: CIPO is a rare, severe, and under-recognized disease. Standardization of treatment strategies, including palliative care and psychiatric interventions, is desired.
Keywords: Decompression; Depression; Intestinal pseudo-obstruction; Palliative care; Total parenteral nutrition.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of percutaneous endoscopic gastro-jejunostomy (PEG-J) decompression therapy for patients with chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction (CIPO).Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2017 Dec;29(12). doi: 10.1111/nmo.13127. Epub 2017 Jun 20. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2017. PMID: 28631871 Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical importance of cine-MRI assessment of small bowel motility in patients with chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction: a retrospective study of 33 patients.J Gastroenterol. 2017 May;52(5):577-584. doi: 10.1007/s00535-016-1251-8. Epub 2016 Aug 22. J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 27549243
-
The chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction subtype has prognostic significance in patients with severe gastrointestinal dysmotility related intestinal failure.Clin Nutr. 2018 Dec;37(6 Pt A):1967-1975. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2018.09.008. Epub 2018 Sep 22. Clin Nutr. 2018. PMID: 30290972
-
[Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction].Nihon Rinsho. 2015 May;73(5):875-83. Nihon Rinsho. 2015. PMID: 25985646 Review. Japanese.
-
Latest developments in chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction.World J Clin Cases. 2020 Dec 6;8(23):5852-5865. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i23.5852. World J Clin Cases. 2020. PMID: 33344584 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Conditions that mimic Hirschsprung's disease, but that are not Hirschsprung's disease.World J Pediatr Surg. 2025 Mar 12;8(1):e000918. doi: 10.1136/wjps-2024-000918. eCollection 2025. World J Pediatr Surg. 2025. PMID: 40094120 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of rifaximin in patients with chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase II-a exploratory trial.Biosci Microbiota Food Health. 2024;43(2):135-144. doi: 10.12938/bmfh.2023-080. Epub 2023 Dec 27. Biosci Microbiota Food Health. 2024. PMID: 38562545 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction due to adult-onset acquired isolated hypoganglionosis with muscular atrophy in the small intestine: a case report and review of literature.Clin J Gastroenterol. 2024 Apr;17(2):244-252. doi: 10.1007/s12328-023-01902-x. Epub 2024 Jan 9. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38193986 Review.
-
Use of Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN) as a Vehicle for Drug Delivery.Curr Drug Targets. 2024;25(5):306-329. doi: 10.2174/0113894501284598240226102943. Curr Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 38454772 Review.
References
-
- Anuras S, Baker CR., Jr The colon in the pseudoobstructive syndrome. Clin Gastroenterol. 1986;15:745–762. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

