Saikosaponin A protects against uremic toxin indole‑3 acetic acid‑induced damage to the myocardium
- PMID: 37417356
- PMCID: PMC10407609
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2023.13046
Saikosaponin A protects against uremic toxin indole‑3 acetic acid‑induced damage to the myocardium
Abstract
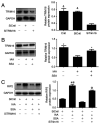
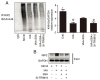
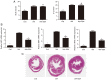
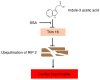
Chronic kidney disease (CKD)‑associated cardiac injury is a common complication in patients with CKD. Indole‑3 acetic acid (IAA) is a uremic toxin that injures the cardiovascular system. Saikosaponin A (SSA) protects against pressure overload‑induced cardiac fibrosis. However, the role and molecular mechanisms of IAA and SSA in CKD‑associated cardiac injury remain unclear. The present study investigated the effects of IAA and SSA on CKD‑associated cardiac injury in neonatal mouse cardiomyocytes and a mouse model of CKD. The expression of tripartite motif‑containing protein 16 (Trim16), receptor interacting protein kinase 2 (RIP2) and phosphorylated‑p38 were assessed using western blotting. The ubiquitination of RIP2 was measured by coimmunoprecipitation, and mouse cardiac structure and function were evaluated using hematoxylin and eosin staining and echocardiography. The results demonstrated that, SSA inhibited IAA‑induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy, upregulated Trim16 expression, downregulated RIP2 expression and decreased p38 phosphorylation. Furthermore, Trim16 mediated SSA‑induced degradation of RIP2 by ubiquitination. In a mouse model of IAA‑induced CKD‑associated cardiac injury, SSA upregulated the protein expression levels of Trim16 and downregulated those of RIP2. Moreover, SSA alleviated heart hypertrophy and diastolic dysfunction in IAA‑treated mice. Taken together, these results suggest that SSA is a protective agent against IAA‑induced CKD‑associated cardiac injury and that Trim16‑mediated ubiquitination‑related degradation of RIP2 and p38 phosphorylation may contribute to the development of CKD‑associated cardiac injury.
Keywords: cardiac injury; chronic kidney disease; indole‑3 acetic acid; saikosaponin A.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Damage of uremic myocardium by p-cresyl sulfate and the ameliorative effect of Klotho by regulating SIRT6 ubiquitination.Toxicol Lett. 2022 Aug 15;367:19-31. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2022.06.006. Epub 2022 Jul 13. Toxicol Lett. 2022. PMID: 35839976
-
Saikosaponin A Protects From Pressure Overload-Induced Cardiac Fibrosis via Inhibiting Fibroblast Activation or Endothelial Cell EndMT.Int J Biol Sci. 2018 Oct 31;14(13):1923-1934. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.27022. eCollection 2018. Int J Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30443195 Free PMC article.
-
Indole-3-acetic acid exposure leads to cardiovascular inflammation and fibrosis in chronic kidney disease rat model.Food Chem Toxicol. 2024 Oct;192:114917. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2024.114917. Epub 2024 Aug 13. Food Chem Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39128690
-
The Role of Gut-Derived, Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins in the Cardiovascular Complications of Acute Kidney Injury.Toxins (Basel). 2022 May 11;14(5):336. doi: 10.3390/toxins14050336. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35622583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of murine models of uremic cardiomyopathy.Kidney Int. 2022 Feb;101(2):256-273. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2021.10.025. Epub 2021 Nov 11. Kidney Int. 2022. PMID: 34774555
Cited by
-
Intestinal microbiota and metabolome perturbations in ischemic and idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy.J Transl Med. 2024 Jan 22;22(1):89. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04605-6. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38254195 Free PMC article.
-
Renal-Cardiac Crosstalk in the Pathogenesis and Progression of Heart Failure.Circ Res. 2025 May 23;136(11):1306-1334. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.124.325488. Epub 2025 May 22. Circ Res. 2025. PMID: 40403103 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

