Extrinsic and intrinsic modulators of inflammation-resolution signaling in heart failure
- PMID: 37417877
- PMCID: PMC10538986
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00276.2023
Extrinsic and intrinsic modulators of inflammation-resolution signaling in heart failure
Abstract
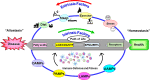
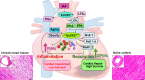
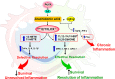
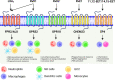
Chronic and uncleared inflammation is the root cause of various cardiovascular diseases. Fundamentally, acute inflammation is supportive when overlapping with safe clearance of inflammation termed resolution; however, if the lifestyle-directed extrinsic factors such as diet, sleep, exercise, or physical activity are misaligned, that results in unresolved inflammation. Although genetics play a critical role in cardiovascular health, four extrinsic risk factors-unhealthy processed diet, sleep disruption or fragmentation, sedentary lifestyle, thereby, subsequent stress-have been identified as heterogeneous and polygenic triggers of heart failure (HF), which can result in several complications with indications of chronic inflammation. Extrinsic risk factors directly impact endogenous intrinsic factors, such as using fatty acids by immune-responsive enzymes [lipoxygenases (LOXs)/cyclooxygenases (COXs)/cytochromes-P450 (CYP450)] to form resolution mediators that activate specific resolution receptors. Thus, the balance of extrinsic factors such as diet, sleep, and physical activity feed-forward the coordination of intrinsic factors such as fatty acids-enzymes-bioactive lipid receptors that modulates the immune defense, metabolic health, inflammation-resolution signaling, and cardiac health. Future research on lifestyle- and aging-associated molecular patterns is warranted in the context of intrinsic and extrinsic factors, immune fitness, inflammation-resolution signaling, and cardiac health.
Keywords: chronic inflammation; heart failure; inflammation-resolution signaling; intrinsic-extrinsic factors; lifestyle-associated molecular patterns.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exercise reduces pro-inflammatory lipids and preserves resolution mediators that calibrate macrophage-centric immune metabolism in spleen and heart following obesogenic diet in aging mice.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2024 Mar;188:79-89. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2024.02.004. Epub 2024 Feb 15. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38364731
-
Inflammation and resolution signaling in cardiac repair and heart failure.EBioMedicine. 2022 May;79:103992. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.103992. Epub 2022 Apr 8. EBioMedicine. 2022. PMID: 35405389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation of EP4 receptor limits transition of acute to chronic heart failure in lipoxygenase deficient mice.Theranostics. 2021 Jan 1;11(6):2742-2754. doi: 10.7150/thno.51183. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33456570 Free PMC article.
-
Lack of resolution sensor drives age-related cardiometabolic and cardiorenal defects and impedes inflammation-resolution in heart failure.Mol Metab. 2020 Jan;31:138-149. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2019.10.008. Epub 2019 Nov 16. Mol Metab. 2020. PMID: 31918915 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic signals and innate immune activation in obesity and exercise.Exerc Immunol Rev. 2015;21:58-68. Exerc Immunol Rev. 2015. PMID: 25825956 Review.
Cited by
-
Neurovascular coupling impairment as a mechanism for cognitive deficits in COVID-19.Brain Commun. 2024 Mar 7;6(2):fcae080. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcae080. eCollection 2024. Brain Commun. 2024. PMID: 38495306 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypertrophic heart failure promotes gut dysbiosis and gut leakage in interleukin 10-deficient mice.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2025 Mar 1;328(3):H447-H459. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00323.2024. Epub 2025 Jan 24. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2025. PMID: 39854049 Free PMC article.
-
Current anti-inflammatory strategies for treatment of heart failure: From innate to adaptive immunity.Pharmacol Res. 2025 Jun;216:107761. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2025.107761. Epub 2025 May 8. Pharmacol Res. 2025. PMID: 40348101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic deletion of 12/15 lipoxygenase delays vascular remodeling and limits cardiorenal dysfunction after pressure overload.J Mol Cell Cardiol Plus. 2023 Aug 19;5:100046. doi: 10.1016/j.jmccpl.2023.100046. eCollection 2023 Sep. J Mol Cell Cardiol Plus. 2023. PMID: 39802176 Free PMC article.
-
Mendelian randomization of plasma lipidome, inflammatory proteome and heart failure.ESC Heart Fail. 2024 Dec;11(6):4209-4221. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.14997. Epub 2024 Aug 15. ESC Heart Fail. 2024. PMID: 39145416 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arnett DK, Blumenthal RS, Albert MA, Buroker AB, Goldberger ZD, Hahn EJ, Himmelfarb CD, Khera A, Lloyd-Jones D, McEvoy JW, Michos ED, Miedema MD, Muñoz D, Smith SC, Virani SS, Williams KA, Yeboah J, Ziaeian B. 2019 ACC/AHA guideline on the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 140: e596–e646, 2019. [Erratum in Circulation 140: e649–e650, 2019]. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000678. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kain V, Van Der Pol W, Mariappan N, Ahmad A, Eipers P, Gibson DL, Gladine C, Vigor C, Durand T, Morrow C, Halade GV. Obesogenic diet in aging mice disrupts gut microbe composition and alters neutrophil:lymphocyte ratio, leading to inflamed milieu in acute heart failure. FASEB J 33: 6456–6469, 2019. doi:10.1096/fj.201802477R. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Khera AV, Emdin CA, Drake I, Natarajan P, Bick AG, Cook NR, Chasman DI, Baber U, Mehran R, Rader DJ, Fuster V, Boerwinkle E, Melander O, Orho-Melander M, Ridker PM, Kathiresan S. Genetic risk, adherence to a healthy lifestyle, and coronary disease. N Engl J Med 375: 2349–2358, 2016. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1605086. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

