Prior expectation enhances sensorimotor behavior by modulating population tuning and subspace activity in sensory cortex
- PMID: 37418521
- PMCID: PMC10328413
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adg4156
Prior expectation enhances sensorimotor behavior by modulating population tuning and subspace activity in sensory cortex
Abstract
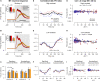
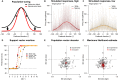
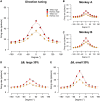
Prior knowledge facilitates our perception and goal-directed behaviors, particularly when sensory input is lacking or noisy. However, the neural mechanisms underlying the improvement in sensorimotor behavior by prior expectations remain unknown. In this study, we examine the neural activity in the middle temporal (MT) area of visual cortex while monkeys perform a smooth pursuit eye movement task with prior expectation of the visual target's motion direction. Prior expectations discriminately reduce the MT neural responses depending on their preferred directions, when the sensory evidence is weak. This response reduction effectively sharpens neural population direction tuning. Simulations with a realistic MT population demonstrate that sharpening the tuning can explain the biases and variabilities in smooth pursuit, suggesting that neural computations in the sensory area alone can underpin the integration of prior knowledge and sensory evidence. State-space analysis further supports this by revealing neural signals of prior expectations in the MT population activity that correlate with behavioral changes.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Expectations about motion direction affect perception and anticipatory smooth pursuit differently.J Neurophysiol. 2021 Mar 1;125(3):977-991. doi: 10.1152/jn.00630.2020. Epub 2021 Feb 3. J Neurophysiol. 2021. PMID: 33534656
-
Spatiotemporal Filter for Visual Motion Integration from Pursuit Eye Movements in Humans and Monkeys.J Neurosci. 2017 Feb 8;37(6):1394-1412. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2682-16.2016. Epub 2016 Dec 21. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28003348 Free PMC article.
-
Neural correlates of prior expectations of motion in the lateral intraparietal and middle temporal areas.J Neurosci. 2012 Jul 18;32(29):10063-74. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5948-11.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22815520 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive Smooth Pursuit Eye Movements.Annu Rev Vis Sci. 2019 Sep 15;5:223-246. doi: 10.1146/annurev-vision-091718-014901. Epub 2019 Jul 5. Annu Rev Vis Sci. 2019. PMID: 31283450 Review.
-
The neuronal basis of on-line visual control in smooth pursuit eye movements.Vision Res. 2015 May;110(Pt B):257-64. doi: 10.1016/j.visres.2014.06.008. Epub 2014 Jul 1. Vision Res. 2015. PMID: 24995378 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Coordinated representations for naturalistic memory encoding and retrieval in hippocampal neural subspaces.Nat Commun. 2025 Jan 14;16(1):641. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-55833-x. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 39809735 Free PMC article.
-
Brain-wide representations of prior information in mouse decision-making.Nature. 2025 Sep;645(8079):192-200. doi: 10.1038/s41586-025-09226-1. Epub 2025 Sep 3. Nature. 2025. PMID: 40903597 Free PMC article.
-
Compositional architecture: Orthogonal neural codes for task context and spatial memory in prefrontal cortex.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Feb 26:2025.02.25.640211. doi: 10.1101/2025.02.25.640211. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40060470 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Localized and global representation of prior value, sensory evidence, and choice in male mouse cerebral cortex.Nat Commun. 2024 May 22;15(1):4071. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-48338-6. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38778078 Free PMC article.
References
-
- A. A. Stocker, E. P. Simoncelli, Noise characteristics and prior expectations in human visual speed perception. Nat. Neurosci. 9, 578–585 (2006). - PubMed
-
- W. J. Ma, Organizing probabilistic models of perception. Trends Cogn. Sci. 16, 511–518 (2012). - PubMed
-
- L.-Q. Zhang, A. Stocker, Psychophysically estimated low-speed prior expectations match the encoding characteristics of neurons in area MT. J. Vis. 21, 2012 (2021).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

