Essential autoproteolysis of bacterial anti-σ factor RsgI for transmembrane signal transduction
- PMID: 37418529
- PMCID: PMC10328401
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adg4846
Essential autoproteolysis of bacterial anti-σ factor RsgI for transmembrane signal transduction
Abstract
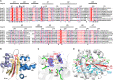
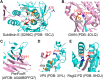
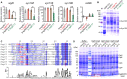
Autoproteolysis has been discovered to play key roles in various biological processes, but functional autoproteolysis has been rarely reported for transmembrane signaling in prokaryotes. In this study, an autoproteolytic effect was discovered in the conserved periplasmic domain of anti-σ factor RsgIs from Clostridium thermocellum, which was found to transmit extracellular polysaccharide-sensing signals into cells for regulation of the cellulosome system, a polysaccharide-degrading multienzyme complex. Crystal and NMR structures of periplasmic domains from three RsgIs demonstrated that they are different from all known proteins that undergo autoproteolysis. The RsgI-based autocleavage site was located at a conserved Asn-Pro motif between the β1 and β2 strands in the periplasmic domain. This cleavage was demonstrated to be essential for subsequent regulated intramembrane proteolysis to activate the cognate SigI, in a manner similar to that of autoproteolysis-dependent activation of eukaryotic adhesion G protein-coupled receptors. These results indicate the presence of a unique prevalent type of autoproteolytic phenomenon in bacteria for signal transduction.
Figures



References
-
- S. C. Jain, U. Shinde, Y. Li, M. Inouye, H. M. Berman, The crystal structure of an autoprocessed Ser221Cys-subtilisin E-propeptide complex at 2.0 Å resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 284, 137–144 (1998). - PubMed
-
- H. Ikemura, M. Inouye, In vitro processing of pro-subtilisin produced in Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 263, 12959–12963 (1988). - PubMed
-
- K. C. Bastiaansen, J. R. Otero-Asman, J. Luirink, W. Bitter, M. A. Llamas, Processing of cell-surface signalling anti-sigma factors prior to signal recognition is a conserved autoproteolytic mechanism that produces two functional domains. Environ. Microbiol. 17, 3263–3277 (2015). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

