Serial Femtosecond Crystallography Reveals that Photoactivation in a Fluorescent Protein Proceeds via the Hula Twist Mechanism
- PMID: 37418747
- PMCID: PMC10375524
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.3c02313
Serial Femtosecond Crystallography Reveals that Photoactivation in a Fluorescent Protein Proceeds via the Hula Twist Mechanism
Abstract
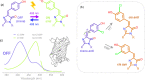
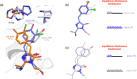
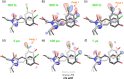
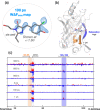
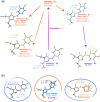
Chromophore cis/trans photoisomerization is a fundamental process in chemistry and in the activation of many photosensitive proteins. A major task is understanding the effect of the protein environment on the efficiency and direction of this reaction compared to what is observed in the gas and solution phases. In this study, we set out to visualize the hula twist (HT) mechanism in a fluorescent protein, which is hypothesized to be the preferred mechanism in a spatially constrained binding pocket. We use a chlorine substituent to break the twofold symmetry of the embedded phenolic group of the chromophore and unambiguously identify the HT primary photoproduct. Through serial femtosecond crystallography, we then track the photoreaction from femtoseconds to the microsecond regime. We observe signals for the photoisomerization of the chromophore as early as 300 fs, obtaining the first experimental structural evidence of the HT mechanism in a protein on its femtosecond-to-picosecond timescale. We are then able to follow how chromophore isomerization and twisting lead to secondary structure rearrangements of the protein β-barrel across the time window of our measurements.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


References
-
- Kandori H. Retinal Proteins: Photochemistry and Optogenetics. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2020, 93, 76–85. 10.1246/bcsj.20190292. - DOI
-
- Mishra K.; Fuenzalida-Werner J. P.; Pennacchietti F.; Janowski R.; Chmyrov A.; Huang Y.; Zakian C.; Klemm U.; Testa I.; Niessing D.; et al. Genetically encoded photo-switchable molecular sensors for optoacoustic and super-resolution imaging. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 598–605. 10.1038/s41587-021-01100-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

