Women's perinatal depression: Anhedonia-related symptoms have increased in the COVID-19 pandemic
- PMID: 37419029
- PMCID: PMC10287182
- DOI: 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2023.06.007
Women's perinatal depression: Anhedonia-related symptoms have increased in the COVID-19 pandemic
Abstract
Background: The prevalence of perinatal depression increased during the COVID-19 pandemic, which may be due to changes in the profile of specific depressive symptoms.
Aims: To analyze the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the (1) prevalence and severity of specific depressive symptoms; and on the (2) prevalence of clinically significant symptoms of depression during pregnancy and postpartum.
Methods: Pregnant and postpartum women recruited before (n = 2395) and during the COVID-19 pandemic (n = 1396) completed a sociodemographic and obstetric questionnaire and the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale (EPDS). For each item, scores ≥1 and ≥ 2 were used to calculate the prevalence and severity of depressive symptoms, respectively.
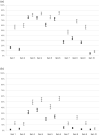
Results: The prevalence and severity of symptoms of depression were significantly higher during the COVID-19 pandemic. The prevalence of specific symptoms increased by >30%, namely "being able to laugh and see the funny side of things" (pregnancy 32.6%, postpartum 40.6%), "looking forward with enjoyment to things" (pregnancy 37.2%, postpartum 47.2%); and "feelings of sadness/miserable" or "unhappiness leading to crying" during postpartum (34.2% and 30.2%, respectively). A substantial increase was observed in the severity of specific symptoms related to feelings that "things have been getting on top of me" during pregnancy and the postpartum period (19.4% and 31.6%, respectively); "feeling sad or miserable" during pregnancy (10.8%); and "feeling scared/panicky" during postpartum (21.4%).
Conclusion: Special attention should be paid to anhedonia-related symptoms of perinatal depression to ensure that they are adequately managed in present and future situations of crisis.
Keywords: COVID-19 pandemic; Postpartum; Pregnancy; Prevalence; Severity; Symptoms of depression.
Copyright © 2023. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest None.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization . Geneva World Health Organization Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0. 2020. The impact of COVID-19 on mental, neurological and substance use services: results of a rapid assessment.
-
- Chmielewska B., Barratt I., Townsend R., Kalafat E., van der Meulen J., Gurol-Urganci I., et al. Effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on maternal and perinatal outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2021;9(6):e759–e772. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(21)00079-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed

