Perspective: A Conceptual Framework for Adaptive Personalized Nutrition Advice Systems (APNASs)
- PMID: 37419418
- PMCID: PMC10509404
- DOI: 10.1016/j.advnut.2023.06.009
Perspective: A Conceptual Framework for Adaptive Personalized Nutrition Advice Systems (APNASs)
Abstract
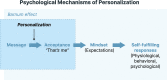
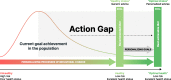
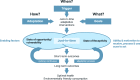
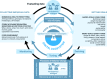
Nearly all approaches to personalized nutrition (PN) use information such as the gene variants of individuals to deliver advice that is more beneficial than a generic "1-size-fits-all" recommendation. Despite great enthusiasm and the increased availability of commercial services, thus far, scientific studies have only revealed small to negligible effects on the efficacy and effectiveness of personalized dietary recommendations, even when using genetic or other individual information. In addition, from a public health perspective, scholars are critical of PN because it primarily targets socially privileged groups rather than the general population, thereby potentially widening health inequality. Therefore, in this perspective, we propose to extend current PN approaches by creating adaptive personalized nutrition advice systems (APNASs) that are tailored to the type and timing of personalized advice for individual needs, capacities, and receptivity in real-life food environments. These systems encompass a broadening of current PN goals (i.e., what should be achieved) to incorporate "individual goal preferences" beyond currently advocated biomedical targets (e.g., making sustainable food choices). Moreover, they cover the "personalization processes of behavior change" by providing in situ, "just-in-time" information in real-life environments (how and when to change), which accounts for individual capacities and constraints (e.g., economic resources). Finally, they are concerned with a "participatory dialog between individuals and experts" (e.g., actual or virtual dieticians, nutritionists, and advisors) when setting goals and deriving measures of adaption. Within this framework, emerging digital nutrition ecosystems enable continuous, real-time monitoring, advice, and support in food environments from exposure to consumption. We present this vision of a novel PN framework along with scenarios and arguments that describe its potential to efficiently address individual and population needs and target groups that would benefit most from its implementation.
Keywords: advice; behavior change; digital ecosystem; dynamic system; food environment; framework; just-in-time adaptive intervention; personalized nutrition; public health.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Personalising dietary advice for disease prevention: concepts and experiences.Pflugers Arch. 2025 Mar;477(3):335-339. doi: 10.1007/s00424-025-03064-w. Epub 2025 Jan 25. Pflugers Arch. 2025. PMID: 39856267 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perspective: Guiding Principles for the Implementation of Personalized Nutrition Approaches That Benefit Health and Function.Adv Nutr. 2020 Jan 1;11(1):25-34. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmz086. Adv Nutr. 2020. PMID: 31504115 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of Web-Based Personalized Nutrition Advice for Adults Using the eNutri Web App: Evidence From the EatWellUK Randomized Controlled Trial.J Med Internet Res. 2022 Apr 25;24(4):e29088. doi: 10.2196/29088. J Med Internet Res. 2022. PMID: 35468093 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Design Issues in Personalized Nutrition Advice Systems.J Med Internet Res. 2023 Mar 29;25:e37667. doi: 10.2196/37667. J Med Internet Res. 2023. PMID: 36989039 Free PMC article.
-
Genetics and Epigenetics in Personalized Nutrition: Evidence, Expectations, and Experiences.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2022 Sep;66(17):e2200077. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.202200077. Epub 2022 Jul 10. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2022. PMID: 35770348 Review.
Cited by
-
Perspective on the ethics of AI at the intersection of nutrition and behaviour change.Front Aging. 2025 May 9;6:1423759. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2025.1423759. eCollection 2025. Front Aging. 2025. PMID: 40417630 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning and personalized nutrition: a promising liaison?Eur J Clin Nutr. 2024 Jan;78(1):74-76. doi: 10.1038/s41430-023-01350-3. Epub 2023 Oct 13. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2024. PMID: 37833568 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The future backbone of nutritional science: integrating public health priorities with system-oriented precision nutrition.Br J Nutr. 2024 Sep 14;132(5):651-666. doi: 10.1017/S0007114524001466. Epub 2024 Sep 25. Br J Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39320518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Personalising dietary advice for disease prevention: concepts and experiences.Pflugers Arch. 2025 Mar;477(3):335-339. doi: 10.1007/s00424-025-03064-w. Epub 2025 Jan 25. Pflugers Arch. 2025. PMID: 39856267 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Data in Personalized Nutrition: Bridging Biomedical, Psycho-behavioral, and Food Environment Approaches for Population-wide Impact.Adv Nutr. 2025 Jul;16(7):100377. doi: 10.1016/j.advnut.2025.100377. Epub 2025 Jan 20. Adv Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39842719 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Levenstein H. University of Chicago Press; Chicago: 2012. Fear of food: A history of why we worry about what we eat.
-
- Zeevi D., Korem T., Zmora N., Israeli D., Rothschild D., Weinberge A., et al. Personalized nutrition by prediction of glycemic responses. Cell. 2015;163(5):1079–1094. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

