Expression of MyHC-15 and -2x in human muscle spindles: An immunohistochemical study
- PMID: 37420120
- PMCID: PMC10557391
- DOI: 10.1111/joa.13923
Expression of MyHC-15 and -2x in human muscle spindles: An immunohistochemical study
Abstract
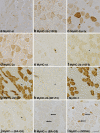
To build on the existing data on the pattern of myosin heavy chain (MyHC) isoforms expression in the human muscle spindles, we aimed to verify whether the 'novel' MyHC-15, -2x and -2b isoforms are co-expressed with the other known isoforms in the human intrafusal fibres. Using a set of antibodies, we attempted to demonstrate nine isoforms (15, slow-tonic, 1, α, 2a, 2x, 2b, embryonic, neonatal) in different regions of intrafusal fibres in the biceps brachii and flexor digitorum profundus muscles. The reactivity of some antibodies with the extrafusal fibres was also tested in the masseter and laryngeal cricothyreoid muscles. In both upper limb muscles, the expression of slow-tonic isoform was a reliable marker for differentiating positive bag fibres from negative chain fibres. Generally, bag1 and bag2 fibres were distinguished in isoform 1 expression; the latter consistently expressed this isoform over their entire length. Although isoform 15 was not abundantly expressed in intrafusal fibres, its expression was pronounced in the extracapsular region of bag fibres. Using a 2x isoform-specific antibody, this isoform was demonstrated in the intracapsular regions of some intrafusal fibres, particularly chain fibres. To the best of our knowledge, this study is the first to demonstrate 15 and 2x isoforms in human intrafusal fibres. However, whether the labelling with an antibody specific for rat 2b isoform reflects the expression of this isoform in bag fibres and some extrafusal ones in the specialised cranial muscles requires further evaluation. The revealed pattern of isoform co-expression only partially agrees with the results of previous, more extensive studies. Nevertheless, it may be inferred that MyHC isoform expression in intrafusal fibres varies along their length, across different muscle spindles and muscles. Furthermore, the estimation of expression may also depend on the antibodies utilised, which may also react differently with intrafusal and extrafusal fibres.
Keywords: immunohistochemistry; intrafusal fibre; muscle spindle; myosin heavy chain isoforms (MyHC); skeletal muscle.
© 2023 The Authors. Journal of Anatomy published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Anatomical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Co-expression of MyHC-15 with other known isoforms in rat muscle spindles.Eur J Histochem. 2025 Jan 21;69(1):4192. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2025.4192. Epub 2025 Mar 24. Eur J Histochem. 2025. PMID: 40126372 Free PMC article.
-
Intrafusal myosin heavy chain expression of human masseter and biceps muscles at young age shows fundamental similarities but also marked differences.Histochem Cell Biol. 2013 Jun;139(6):895-907. doi: 10.1007/s00418-012-1072-7. Epub 2013 Jan 11. Histochem Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23306907
-
Expression of myosin heavy chain isoforms in regenerated muscle spindle fibres after muscle grafting in young and adult rats--plasticity of intrafusal satellite cells.Differentiation. 1997 Dec;62(4):179-86. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-0436.1998.6240179.x. Differentiation. 1997. PMID: 9503602
-
Expression of myosin heavy chain isoforms and myogenesis of intrafusal fibres in rat muscle spindles.Microsc Res Tech. 1995 Apr 1;30(5):390-407. doi: 10.1002/jemt.1070300506. Microsc Res Tech. 1995. PMID: 7787238 Review.
-
Specialized cranial muscles: how different are they from limb and abdominal muscles?Cells Tissues Organs. 2003;174(1-2):73-86. doi: 10.1159/000070576. Cells Tissues Organs. 2003. PMID: 12784043 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Co-expression of MyHC-15 with other known isoforms in rat muscle spindles.Eur J Histochem. 2025 Jan 21;69(1):4192. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2025.4192. Epub 2025 Mar 24. Eur J Histochem. 2025. PMID: 40126372 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Banks, R.W. & Barker, D. (2004) The muscle spindle. In: Engel, A. & Franzini‐Armstrong, C. (Eds.) Myology, 3rd edition. New York: McGraw‐Hill, pp. 489–509.
-
- Bloemink, M.J. , Deacon, J.C. , Resnicow, D.I. , Leinwand, L.A. & Geeves, M.A. (2013) The superfast human extraocular myosin is kinetically distinct from the fast skeletal IIa, IIb, and IId isoforms. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 288(38), 27469–27479. Available from: 10.1074/jbc.M113.488130 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bormioli, S.P. , Torresan, P. , Sartore, S. , Moschini, G.B. & Schiaffino, S. (1979) Immunohistochemical identification of slow‐tonic fibers in human extrinsic eye muscles. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science, 18(3), 303–306. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

