Effect of Orlistat on anthropometrics and metabolic indices in children and adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 37420181
- PMCID: PMC10327388
- DOI: 10.1186/s12902-023-01390-7
Effect of Orlistat on anthropometrics and metabolic indices in children and adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Childhood obesity is one of the main concerns of public health. Considering its long-term adverse health effect, various studies investigated the effect of drug therapy on anthropometric parameters and provided mixed results. In this systematic review and meta-analysis, we aimed to determine the effect of Orlistat on anthropometrics and biochemical parameters in children and adolescents.
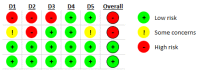
Materials and methods: The databases of PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science were searched until September 2022. Experimental and semi-experimental studies were included if they evaluated the effect of Orlistat on obesity-related parameters in children and reported the before and after anthropometric values. A revised Cochrane risk-of-bias (Rob2) was used to evaluate the methodological quality. STATA software version 16.0 was used for the meta-analysis of the random-effect model.
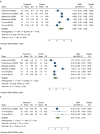
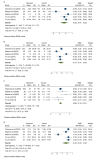
Results: Of 810 articles retrieved in the initial search, four experimental and two semi-experimental studies were selected for systematic review. The result of the meta-analysis of experimental studies indicated the significant effect of Orlistat on waist circumference (SMD: -0.27, 95% CI: -0.47, -0.07) and serum insulin level (SMD: -0.89, 95% CI: -1.52, 0.26). However, there were no significant effects of orlistat on body weight, body mass index, lipid profile, and serum glucose level.
Conclusion: The present meta-analysis showed the significant effect of Orlistat on the reduction of waist circumference and insulin level in overweight and obese adolescents. However, due to the paucity of studies included in the meta-analysis, more prospective studies with longer duration and more sample sizes will be needed in this age group.
Keywords: Adolescents; Anthropometry; Children; Metabolic Indices; Orlistat.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Pharmacological therapy of obesity].G Ital Cardiol (Rome). 2008 Apr;9(4 Suppl 1):83S-93S. G Ital Cardiol (Rome). 2008. PMID: 18773755 Italian.
-
Effects of orlistat on body mass index and serum lipids in overweight and obese adolescents: a meta-analysis.J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2024 Dec 10;38(2):95-101. doi: 10.1515/jpem-2024-0429. Print 2025 Feb 25. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2024. PMID: 39648190
-
Effect of orlistat on weight and body composition in obese adolescents: a randomized controlled trial.JAMA. 2005 Jun 15;293(23):2873-83. doi: 10.1001/jama.293.23.2873. JAMA. 2005. PMID: 15956632 Clinical Trial.
-
Effectiveness of weight management programs in children and adolescents.Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2008 Sep;(170):1-308. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2008. PMID: 19408967 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Short-term administration of orlistat reduced daytime triglyceridemia in obese women with the metabolic syndrome.Angiology. 2007 Feb-Mar;58(1):26-33. doi: 10.1177/0003319706297915. Angiology. 2007. PMID: 17351155 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
The effect of orlistat in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver in adolescents with overweight and obese.Eur J Pediatr. 2024 Mar;183(3):1173-1182. doi: 10.1007/s00431-023-05369-3. Epub 2023 Dec 11. Eur J Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 38081992 Clinical Trial.
-
Association of long-term weight management pharmacotherapy with multiple health outcomes: an umbrella review and evidence map.Int J Obes (Lond). 2025 Mar;49(3):464-477. doi: 10.1038/s41366-025-01719-3. Epub 2025 Jan 26. Int J Obes (Lond). 2025. PMID: 39865161
-
Antiobesity Pharmacotherapy for Patients With Genetic Obesity Due to Defects in the Leptin-Melanocortin Pathway.Endocr Rev. 2025 May 9;46(3):418-446. doi: 10.1210/endrev/bnaf004. Endocr Rev. 2025. PMID: 39929239 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Real -world experience with anti-obesity medications treatment in children and adolescents with overweight and obesity in Israel.Int J Obes (Lond). 2025 Jul;49(7):1390-1399. doi: 10.1038/s41366-025-01801-w. Epub 2025 May 15. Int J Obes (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40374727 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization: Obesity and overweight. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (2021). Accessed 9 June 2021.
-
- Anderson PM, Butcher KF. Childhood obesity: trends and potential causes. The Future of children 2006:19–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

