Enhancing the interferon-γ release assay through omission of nil and mitogen values
- PMID: 37420251
- PMCID: PMC10327336
- DOI: 10.1186/s12931-023-02485-4
Enhancing the interferon-γ release assay through omission of nil and mitogen values
Abstract
Purpose: To address the limited utility of the interferon (IFN)-γ release assay (IGRA) caused by its variability and inconsistency.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study was based on data obtained between 2011 and 2019. QuantiFERON-TB Gold-In-Tube was used to measure IFN-γ levels in nil, tuberculosis (TB) antigen, and mitogen tubes.
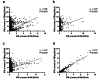
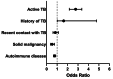
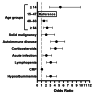
Results: Of 9,378 cases, 431 had active TB. The non-TB group comprised 1,513 IGRA-positive, 7,202 IGRA-negative, and 232 IGRA-indeterminate cases. Nil-tube IFN-γ levels were significantly higher in the active TB group (median = 0.18 IU/mL; interquartile range: 0.09-0.45 IU/mL) than in the IGRA-positive non-TB (0.11 IU/mL; 0.06-0.23 IU/mL) and IGRA-negative non-TB (0.09 IU/mL; 0.05-0.15 IU/mL) groups (P < 0.0001). From receiver operating characteristic analysis, TB antigen tube IFN-γ levels had higher diagnostic utility for active TB than TB antigen minus nil values. In a logistic regression analysis, active TB was the main driver of higher nil values. In the active TB group, after reclassifying the results based on a TB antigen tube IFN-γ level of 0.48 IU/mL, 14/36 cases with negative results and 15/19 cases with indeterminate results became positive, while 1/376 cases with positive results became negative. Overall, the sensitivity for detecting active TB improved from 87.2 to 93.7%.
Conclusion: The results of our comprehensive assessment can aid in IGRA interpretation. Since nil values are governed by TB infection rather than reflecting background noise, TB antigen tube IFN-γ levels should be used without subtracting nil values. Despite indeterminate results, TB antigen tube IFN-γ levels can be informative.
Keywords: Immunological tests; Interferon-γ; Latent tuberculosis; Release assay; Tuberculosis.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

