Healthcare Application of In-Shoe Motion Sensor for Older Adults: Frailty Assessment Using Foot Motion during Gait
- PMID: 37420613
- PMCID: PMC10304868
- DOI: 10.3390/s23125446
Healthcare Application of In-Shoe Motion Sensor for Older Adults: Frailty Assessment Using Foot Motion during Gait
Abstract
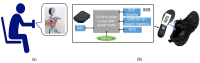
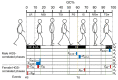
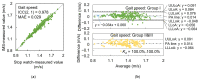
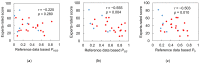
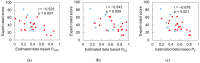
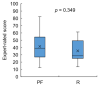
Frailty poses a threat to the daily lives of healthy older adults, highlighting the urgent need for technologies that can monitor and prevent its progression. Our objective is to demonstrate a method for providing long-term daily frailty monitoring using an in-shoe motion sensor (IMS). We undertook two steps to achieve this goal. Firstly, we used our previously established SPM-LOSO-LASSO (SPM: statistical parametric mapping; LOSO: leave-one-subject-out; LASSO: least absolute shrinkage and selection operator) algorithm to construct a lightweight and interpretable hand grip strength (HGS) estimation model for an IMS. This algorithm automatically identified novel and significant gait predictors from foot motion data and selected optimal features to construct the model. We also tested the robustness and effectiveness of the model by recruiting other groups of subjects. Secondly, we designed an analog frailty risk score that combined the performance of the HGS and gait speed with the aid of the distribution of HGS and gait speed of the older Asian population. We then compared the effectiveness of our designed score with the clinical expert-rated score. We discovered new gait predictors for HGS estimation via IMSs and successfully constructed a model with an "excellent" intraclass correlation coefficient and high precision. Moreover, we tested the model on separately recruited subjects, which confirmed the robustness of our model for other older individuals. The designed frailty risk score also had a large effect size correlation with clinical expert-rated scores. In conclusion, IMS technology shows promise for long-term daily frailty monitoring, which can help prevent or manage frailty for older adults.
Keywords: frailty assessment; gait analysis; healthcare application; in-shoe motion sensor; older adults.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures










References
-
- Fritz S., Lusardi M. White paper: “walking speed: The sixth vital sign”. [(accessed on 6 June 2023)];J. Geriatr. Phys. Ther. 2009 32:2–5. doi: 10.1519/00139143-200932020-00002. Available online: https://digitalcommons.sacredheart.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1134&.... - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sialino L.D., Schaap L.A., van Oostrom S.H., Picavet H.S.J., Twisk J.W., Verschuren W., Visser M., Wijnhoven H.A. The sex difference in gait speed among older adults: How do sociodemographic, lifestyle, social and health determinants contribute? BMC Geriatr. 2021;21:340. doi: 10.1186/s12877-021-02279-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

