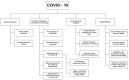
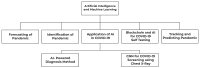
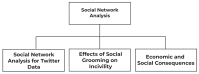
A Survey on COVID-19 Data Analysis Using AI, IoT, and Social Media
- PMID: 37420714
- PMCID: PMC10303179
- DOI: 10.3390/s23125543
A Survey on COVID-19 Data Analysis Using AI, IoT, and Social Media
Abstract
Coronaviruses are a well-established and deadly group of viruses that cause illness in both humans and animals. The novel type of this virus group, named COVID-19, was firstly reported in December 2019, and, with the passage of time, coronavirus has spread to almost all parts of the world. Coronavirus has been the cause of millions of deaths around the world. Furthermore, many countries are struggling with COVID-19 and have experimented with various kinds of vaccines to eliminate the deadly virus and its variants. This survey deals with COVID-19 data analysis and its impact on human social life. Data analysis and information related to coronavirus can greatly help scientists and governments in controlling the spread and symptoms of the deadly coronavirus. In this survey, we cover many areas of discussion related to COVID-19 data analysis, such as how artificial intelligence, along with machine learning, deep learning, and IoT, have worked together to fight against COVID-19. We also discuss artificial intelligence and IoT techniques used to forecast, detect, and diagnose patients of the novel coronavirus. Moreover, this survey also describes how fake news, doctored results, and conspiracy theories were spread over social media sites, such as Twitter, by applying various social network analysis and sentimental analysis techniques. A comprehensive comparative analysis of existing techniques has also been conducted. In the end, the Discussion section presents different data analysis techniques, provides future directions for research, and suggests general guidelines for handling coronavirus, as well as changing work and life conditions.
Keywords: COVID-19; IoT; artificial intelligence; data analysis; epidemic outbreak; social network analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wahid R., Pribadi F., Wakas B.E. Digital Activism: COVID-19 Effects in Campus Learning. Bp. Int. Res. Critics Linguist. Educ. BirLE J. 2020;3:1336–1342. doi: 10.33258/birle.v3i3.1174. - DOI
-
- Worldometer Cases and Deaths from COVID-19 Virus Pandemic. [(accessed on 6 June 2023)]. Available online: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus.
-
- Chen J., Li K., Zhang Z., Li K., Yu P.S. A survey on applications of artificial intelligence in fighting against COVID-19. ACM Comput. Surv. CSUR. 2021;54:1–32. doi: 10.1145/3465398. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical