StethAid: A Digital Auscultation Platform for Pediatrics
- PMID: 37420914
- PMCID: PMC10304273
- DOI: 10.3390/s23125750
StethAid: A Digital Auscultation Platform for Pediatrics
Abstract
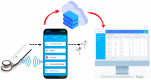
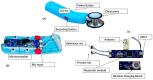
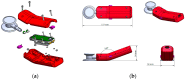
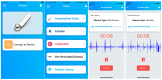
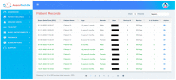
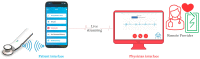
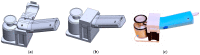
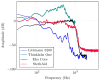
(1) Background: Mastery of auscultation can be challenging for many healthcare providers. Artificial intelligence (AI)-powered digital support is emerging as an aid to assist with the interpretation of auscultated sounds. A few AI-augmented digital stethoscopes exist but none are dedicated to pediatrics. Our goal was to develop a digital auscultation platform for pediatric medicine. (2) Methods: We developed StethAid-a digital platform for artificial intelligence-assisted auscultation and telehealth in pediatrics-that consists of a wireless digital stethoscope, mobile applications, customized patient-provider portals, and deep learning algorithms. To validate the StethAid platform, we characterized our stethoscope and used the platform in two clinical applications: (1) Still's murmur identification and (2) wheeze detection. The platform has been deployed in four children's medical centers to build the first and largest pediatric cardiopulmonary datasets, to our knowledge. We have trained and tested deep-learning models using these datasets. (3) Results: The frequency response of the StethAid stethoscope was comparable to those of the commercially available Eko Core, Thinklabs One, and Littman 3200 stethoscopes. The labels provided by our expert physician offline were in concordance with the labels of providers at the bedside using their acoustic stethoscopes for 79.3% of lungs cases and 98.3% of heart cases. Our deep learning algorithms achieved high sensitivity and specificity for both Still's murmur identification (sensitivity of 91.9% and specificity of 92.6%) and wheeze detection (sensitivity of 83.7% and specificity of 84.4%). (4) Conclusions: Our team has created a technically and clinically validated pediatric digital AI-enabled auscultation platform. Use of our platform could improve efficacy and efficiency of clinical care for pediatric patients, reduce parental anxiety, and result in cost savings.
Keywords: Still’s murmur detection; artificial intelligence-assisted auscultation; deep learning; digital stethoscope; pediatric stethoscope; wheeze detection.
Conflict of interest statement
R.W.D. and R.S. are founders of AusculTech Dx.
Figures
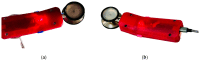
Similar articles
-
Artificial intelligence accuracy in detecting pathological breath sounds in children using digital stethoscopes.Respir Res. 2020 Sep 29;21(1):253. doi: 10.1186/s12931-020-01523-9. Respir Res. 2020. PMID: 32993620 Free PMC article.
-
Digital stethoscopes compared to standard auscultation for detecting abnormal paediatric breath sounds.Eur J Pediatr. 2017 Jul;176(7):989-992. doi: 10.1007/s00431-017-2929-5. Epub 2017 May 16. Eur J Pediatr. 2017. PMID: 28508991 Clinical Trial.
-
Deep Learning Algorithm for Automated Cardiac Murmur Detection via a Digital Stethoscope Platform.J Am Heart Assoc. 2021 May 4;10(9):e019905. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.120.019905. Epub 2021 Apr 26. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021. PMID: 33899504 Free PMC article.
-
The coming era of a new auscultation system for analyzing respiratory sounds.BMC Pulm Med. 2022 Mar 31;22(1):119. doi: 10.1186/s12890-022-01896-1. BMC Pulm Med. 2022. PMID: 35361176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Digital Pulmonology Practice with Phonopulmography Leveraging Artificial Intelligence: Future Perspectives Using Dual Microwave Acoustic Sensing and Imaging.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Jun 12;23(12):5514. doi: 10.3390/s23125514. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37420680 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Noise-Robust Heart Sound Segmentation Algorithm Based on Shannon Energy.IEEE Access. 2024;12:7747-7761. doi: 10.1109/access.2024.3351570. Epub 2024 Jan 8. IEEE Access. 2024. PMID: 39398361 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence and wheezing in children: where are we now?Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Aug 27;11:1460050. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1460050. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39257890 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deep Learning in Heart Sound Analysis: From Techniques to Clinical Applications.Health Data Sci. 2024 Oct 9;4:0182. doi: 10.34133/hds.0182. eCollection 2024. Health Data Sci. 2024. PMID: 39387057 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Automated Detection of Reduced Ejection Fraction Using an ECG-Enabled Digital Stethoscope: A Large Cohort Validation.JACC Adv. 2025 Mar;4(3):101619. doi: 10.1016/j.jacadv.2025.101619. Epub 2025 Feb 20. JACC Adv. 2025. PMID: 39983614 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Intelligence-Driven Wireless Sensing for Health Management.Bioengineering (Basel). 2025 Feb 27;12(3):244. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering12030244. Bioengineering (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40150708 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

