Smart Chemical Sensor and Biosensor Networks for Healthcare 4.0
- PMID: 37420917
- PMCID: PMC10303589
- DOI: 10.3390/s23125754
Smart Chemical Sensor and Biosensor Networks for Healthcare 4.0
Abstract
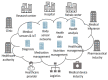
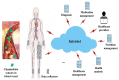
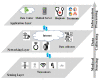
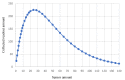
Driven by technological advances from Industry 4.0, Healthcare 4.0 synthesizes medical sensors, artificial intelligence (AI), big data, the Internet of things (IoT), machine learning, and augmented reality (AR) to transform the healthcare sector. Healthcare 4.0 creates a smart health network by connecting patients, medical devices, hospitals, clinics, medical suppliers, and other healthcare-related components. Body chemical sensor and biosensor networks (BSNs) provide the necessary platform for Healthcare 4.0 to collect various medical data from patients. BSN is the foundation of Healthcare 4.0 in raw data detection and information collecting. This paper proposes a BSN architecture with chemical sensors and biosensors to detect and communicate physiological measurements of human bodies. These measurement data help healthcare professionals to monitor patient vital signs and other medical conditions. The collected data facilitates disease diagnosis and injury detection at an early stage. Our work further formulates the problem of sensor deployment in BSNs as a mathematical model. This model includes parameter and constraint sets to describe patient body characteristics, BSN sensor features, as well as biomedical readout requirements. The proposed model's performance is evaluated by multiple sets of simulations on different parts of the human body. Simulations are designed to represent typical BSN applications in Healthcare 4.0. Simulation results demonstrate the impact of various biofactors and measurement time on sensor selections and readout performance.
Keywords: Healthcare 4.0; Industry 4.0; biosensors; blood flow velocity; body chemical sensors and biosensor networks (BSNs); chemical sensors; heel inflammation; monitoring time; runner’s knee; sensor; shin splints; successful number of readouts; tennis elbow; wearable data collector; wearable devices.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Artificial Intelligence Based Body Sensor Network Framework-Narrative Review: Proposing an End-to-End Framework using Wearable Sensors, Real-Time Location Systems and Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning Algorithms for Data Collection, Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery in Sports and Healthcare.Sports Med Open. 2021 Oct 30;7(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s40798-021-00372-0. Sports Med Open. 2021. PMID: 34716868 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AI-driven adaptive reliable and sustainable approach for internet of things enabled healthcare system.Math Biosci Eng. 2022 Feb 11;19(4):3953-3971. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2022182. Math Biosci Eng. 2022. PMID: 35341282
-
Enhancing Healthcare through Sensor-Enabled Digital Twins in Smart Environments: A Comprehensive Analysis.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Apr 27;24(9):2793. doi: 10.3390/s24092793. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38732899 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial intelligence biosensors: Challenges and prospects.Biosens Bioelectron. 2020 Oct 1;165:112412. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2020.112412. Epub 2020 Jul 3. Biosens Bioelectron. 2020. PMID: 32729531 Review.
-
The Emergence of AI-Based Wearable Sensors for Digital Health Technology: A Review.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Nov 29;23(23):9498. doi: 10.3390/s23239498. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38067871 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An FPGA-Based SiNW-FET Biosensing System for Real-Time Viral Detection: Hardware Amplification and 1D CNN for Adaptive Noise Reduction.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Jan 3;25(1):236. doi: 10.3390/s25010236. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39797026 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence-powered electrochemical sensor: Recent advances, challenges, and prospects.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 14;10(18):e37964. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37964. eCollection 2024 Sep 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39328566 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Internet of Medical Things and Healthcare 4.0: Trends, Requirements, Challenges, and Research Directions.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Aug 25;23(17):7435. doi: 10.3390/s23177435. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37687891 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Qiu T., Li B., Qu W., Ahmed E., Wang X. TOSG: A topology optimization scheme with global small world for industrial heterogeneous internet of things. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019;15:3174–3184. doi: 10.1109/TII.2018.2872579. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

