Identification of the Position of a Tethered Delivery Catheter to Retrieve an Untethered Magnetic Robot in a Vascular Environment
- PMID: 37420957
- PMCID: PMC10143211
- DOI: 10.3390/mi14040724
Identification of the Position of a Tethered Delivery Catheter to Retrieve an Untethered Magnetic Robot in a Vascular Environment
Abstract
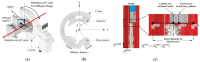
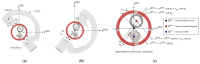
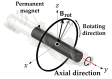
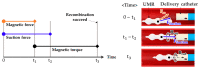
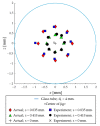
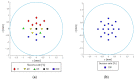
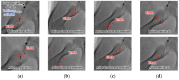
In this paper, we propose a method of identifying the position of a tethered delivery catheter in a vascular environment, recombining an untethered magnetic robot (UMR) to the tethered delivery catheter, and safely retrieving them from the vascular environment in an endovascular intervention by utilizing a separable and recombinable magnetic robot (SRMR) and a magnetic navigation system (MNS). From images of a blood vessel and a tethered delivery catheter taken from two different angles, we developed a method of extracting the position of the delivery catheter in the blood vessel by introducing dimensionless cross-sectional coordinates. Then, we propose a retrieval method for the UMR by using the magnetic force considering the delivery catheter's position, suction force, and rotating magnetic field. We used thane MNS and feeding robot to simultaneously apply magnetic force and suction force to the UMR. In this process, we determined a current solution for generating magnetic force by using a linear optimization method. Finally, we conducted in vitro and in vivo experiments to verify the proposed method. In the in vitro experiment, which was in a glass tube environment, by using an RGB camera, we confirmed that the location of the delivery catheter in the glass tube could be recognized within an average error of 0.05 mm in each of the X- and Z-coordinates and that the retrieval success rate was greatly improved in comparison with that in the case without the use of magnetic force. In an in vivo experiment, we successfully retrieved the UMR in the femoral arteries of pigs.
Keywords: position identification; retrieval of an untethered magnetic robot; vascular environment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
A 5-D Localization Method for a Magnetically Manipulated Untethered Robot using a 2-D Array of Hall-effect Sensors.IEEE ASME Trans Mechatron. 2016 Apr;21(2):708-716. doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2015.2488361. Epub 2016 Mar 1. IEEE ASME Trans Mechatron. 2016. PMID: 27458327 Free PMC article.
-
Real-Time Ultrasound Doppler Tracking and Autonomous Navigation of a Miniature Helical Robot for Accelerating Thrombolysis in Dynamic Blood Flow.ACS Nano. 2022 Jan 25;16(1):604-616. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.1c07830. Epub 2022 Jan 4. ACS Nano. 2022. PMID: 34985859
-
Remote-controlled vascular interventional surgery robot.Int J Med Robot. 2010 Jun;6(2):194-201. doi: 10.1002/rcs.306. Int J Med Robot. 2010. PMID: 20235338
-
Electrical Optimization Method Based on a Novel Arrangement of the Magnetic Navigation System with Gradient and Uniform Saddle Coils.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Jul 27;22(15):5603. doi: 10.3390/s22155603. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35898106 Free PMC article.
-
Design and performance evaluation of collision protection-based safety operation for a haptic robot-assisted catheter operating system.Biomed Microdevices. 2018 Feb 23;20(2):22. doi: 10.1007/s10544-018-0266-8. Biomed Microdevices. 2018. PMID: 29476379 Review.
References
-
- Gnatiuc L., Herrington W.G. Sex-specific relevance of diabetes to occlusive vascular and other mortality: A collaborative meta-analysis of individual data from 980 793 adults from 68 prospective studies. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018;6:538–546. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(18)30079-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ali K., Kruse M.J. Guidewires, catheters, and sheaths used for thoracic endografting procedures. J. Card. Surg. 2009;24:113–119. - PubMed
-
- Hwang J., Kim J.Y., Choi H. A review of magnetic actuation systems and magnetically actuated guidewire-and catheter-based microrobots for vascular interventions. Intell. Serv. Robot. 2020;13:1–14. doi: 10.1007/s11370-020-00311-0. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

