A Bi-Directional Acoustic Micropump Driven by Oscillating Sharp-Edge Structures
- PMID: 37421093
- PMCID: PMC10146208
- DOI: 10.3390/mi14040860
A Bi-Directional Acoustic Micropump Driven by Oscillating Sharp-Edge Structures
Abstract
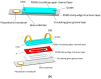
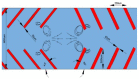
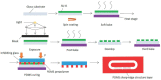
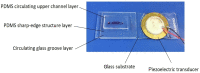
This paper proposes a bi-directional acoustic micropump driven by two groups of oscillating sharp-edge structures: one group of sharp-edge structures with inclined angles of 60° and a width of 40 μm, and another group with inclined angles of 45° and a width of 25 μm. One of the groups of sharp-edge structures will vibrate under the excitation of the acoustic wave generated with a piezoelectric transducer at its corresponding resonant frequency. When one group of sharp-edge structures vibrates, the microfluid flows from left to right. When the other group of sharp-edge structures vibrates, the microfluid flows in the opposite direction. Some gaps are designed between the sharp-edge structures and the upper surface and the bottom surface of the microchannels, which can reduce the damping between the sharp-edge structures and the microchannels. Actuated with an acoustic wave of a different frequency, the microfluid in the microchannel can be driven bidirectionally by the inclined sharp-edge structures. The experiments show that the acoustic micropump, driven by oscillating sharp-edge structures, can produce a stable flow rate of up to 125 μm/s from left to right, when the transducer was activated at 20.0 kHz. When the transducer was activated at 12.8 kHz, the acoustic micropump can produce a stable flow rate of up to 85 μm/s from right to left. This bi-directional acoustic micropump, driven by oscillating sharp-edge structures, is easy to operate and shows great potential in various applications.
Keywords: acoustic wave; bi-directional pump; micropump; sharp-edge structure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Yang Y.W., Wang J.H. The status and application of MEMS technology. Micronanoelectron. Technol. 2023;40:29–32.
-
- Gad-el-Hak M. The fluid mechanics of microdevices—The Freeman scholar lecture. J. Fluids Eng. 1999;121:5–33. doi: 10.1115/1.2822013. - DOI
-
- Ho C.M., Tai Y.C. Micro-electro-mechanical-systems (MEMS) and fluid flows. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1998;30:579–612. doi: 10.1146/annurev.fluid.30.1.579. - DOI
-
- Iverson B.D., Garimella S.V. Recent advances in microscale pumping technologies: A review and evaluation. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2008;5:145–174. doi: 10.1007/s10404-008-0266-8. - DOI
-
- Au A.K., Lai H., Utela B.R., Folch A. Microvalves and micropumps for BioMEMS. Micromachines. 2011;2:179–220. doi: 10.3390/mi2020179. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

