A Brief Review on Cerium Oxide (CeO2NPs)-Based Scaffolds: Recent Advances in Wound Healing Applications
- PMID: 37421098
- PMCID: PMC10143419
- DOI: 10.3390/mi14040865
A Brief Review on Cerium Oxide (CeO2NPs)-Based Scaffolds: Recent Advances in Wound Healing Applications
Abstract
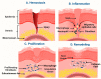
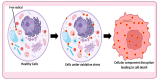
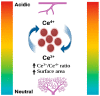
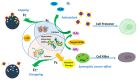
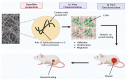
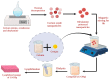
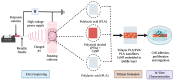
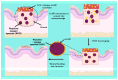
The process of wound healing is complex and involves the interaction of multiple cells, each with a distinct role in the inflammatory, proliferative, and remodeling phases. Chronic, nonhealing wounds may result from reduced fibroblast proliferation, angiogenesis, and cellular immunity, often associated with diabetes, hypertension, vascular deficits, immunological inadequacies, and chronic renal disease. Various strategies and methodologies have been explored to develop nanomaterials for wound-healing treatment. Several nanoparticles such as gold, silver, cerium oxide and zinc possess antibacterial properties, stability, and a high surface area that promotes efficient wound healing. In this review article, we investigate the effectiveness of cerium oxide nanoparticles (CeO2NPs) in wound healing-particularly the effects of reducing inflammation, enhancing hemostasis and proliferation, and scavenging reactive oxygen species. The mechanism enables CeO2NPs to reduce inflammation, modulate the immunological system, and promote angiogenesis and tissue regeneration. In addition, we investigate the efficacy of cerium oxide-based scaffolds in various wound-healing applications for creating a favorable wound-healing environment. Cerium oxide nanoparticles (CeO2NPs) exhibit antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and regenerative characteristics, enabling them to be ideal wound healing material. Investigations have shown that CeO2NPs can stimulate wound closure, tissue regeneration, and scar reduction. CeO2NPs may also reduce bacterial infections and boost wound-site immunity. However, additional study is needed to determine the safety and efficacy of CeO2NPs in wound healing and their long-term impacts on human health and the environment. The review reveals that CeO2NPs have promising wound-healing properties, but further study is needed to understand their mechanisms of action and ensure their safety and efficacy.
Keywords: cerium oxide; scaffolds; skin; wound healing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Biosynthesized Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles CeO2NPs: Recent Progress and Medical Applications.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2023;24(6):766-779. doi: 10.2174/1389201023666220821161737. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36017829 Review.
-
Advancing biomedical applications: antioxidant and biocompatible cerium oxide nanoparticle-integrated poly-ε-caprolactone fibers.Biomed Phys Eng Express. 2024 Dec 3;11(1). doi: 10.1088/2057-1976/ad927f. Biomed Phys Eng Express. 2024. PMID: 39541601
-
Cerium oxide nanoparticles reduce steatosis, portal hypertension and display anti-inflammatory properties in rats with liver fibrosis.J Hepatol. 2016 Mar;64(3):691-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.10.020. Epub 2015 Oct 28. J Hepatol. 2016. PMID: 26519601
-
Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles Protect against Oxidant Injury and Interfere with Oxidative Mediated Kinase Signaling in Human-Derived Hepatocytes.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Nov 27;20(23):5959. doi: 10.3390/ijms20235959. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31783479 Free PMC article.
-
Nanomaterials-based Drug Delivery Approaches for Wound Healing.Curr Pharm Des. 2022;28(9):711-726. doi: 10.2174/1381612828666220328121211. Curr Pharm Des. 2022. PMID: 35345993 Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of the Synthesis Scheme of Nanocrystalline Cerium Oxide and Its Concentration on the Biological Activity of Cells Providing Wound Regeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 24;24(19):14501. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914501. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37833949 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Composite Sponge Scaffolds Based on Carrageenan (CRG) and Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles (CeO2 NPs) for Hemostatic Applications.Biomimetics (Basel). 2023 Sep 4;8(5):409. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics8050409. Biomimetics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37754160 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial for the Special Issue on Biomaterials, Biodevices and Tissue Engineering.Micromachines (Basel). 2024 Apr 30;15(5):604. doi: 10.3390/mi15050604. Micromachines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38793177 Free PMC article.
-
The regulatory mechanisms of cerium oxide nanoparticles in oxidative stress and emerging applications in refractory wound care.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Aug 2;15:1439960. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1439960. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39156103 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cerium oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis methods and applications in wound healing.Mater Today Bio. 2023 Oct 1;23:100823. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2023.100823. eCollection 2023 Dec. Mater Today Bio. 2023. PMID: 37928254 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

