3D Bioprinting of an Endothelialized Liver Lobule-like Construct as a Tumor-Scale Drug Screening Platform
- PMID: 37421111
- PMCID: PMC10146619
- DOI: 10.3390/mi14040878
3D Bioprinting of an Endothelialized Liver Lobule-like Construct as a Tumor-Scale Drug Screening Platform
Abstract
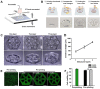
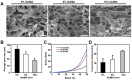
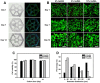
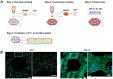
3D cell culture models replicating the complexity of cell-cell interactions and biomimetic extracellular matrix (ECM) are novel approaches for studying liver cancer, including in vitro drug screening or disease mechanism investigation. Although there have been advancements in the production of 3D liver cancer models to serve as drug screening platforms, recreating the structural architecture and tumor-scale microenvironment of native liver tumors remains a challenge. Here, using the dot extrusion printing (DEP) technology reported in our previous work, we fabricated an endothelialized liver lobule-like construct by printing hepatocyte-laden methacryloyl gelatin (GelMA) hydrogel microbeads and HUVEC-laden gelatin microbeads. DEP technology enables hydrogel microbeads to be produced with precise positioning and adjustable scale, facilitating the construction of liver lobule-like structures. The vascular network was achieved by sacrificing the gelatin microbeads at 37 °C to allow HUVEC proliferation on the surface of the hepatocyte layer. Finally, we used the endothelialized liver lobule-like constructs for anti-cancer drug (Sorafenib) screening, and stronger drug resistance results were obtained when compared to either mono-cultured constructs or hepatocyte spheroids alone. The 3D liver cancer models presented here successfully recreate liver lobule-like morphology, and may have the potential to serve as a liver tumor-scale drug screening platform.
Keywords: 3D bioprinting; GelMA hydrogel; drug screening; liver lobule-like construct.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Naghavi M., Wang H., Lozano R., Davis A., Liang X., Zhou M., Vollset S.E., Ozgoren A.A., Abdalla S., Abd-Allah F. Global, regional, and national age-sex specific allcause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2015;385:117–171. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tang W., Chen Z., Zhang W., Cheng Y., Zhang B., Wu F., Wang Q., Wang S., Rong D., Reiter F.P., et al. The mechanisms of sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma: Theoretical basis and therapeutic aspects. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2020;5:87. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-0187-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

