Blood-based T cell receptor anti-viral CDR3s are associated with worse overall survival for neuroblastoma
- PMID: 37421457
- PMCID: PMC11797736
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-023-05059-5
Blood-based T cell receptor anti-viral CDR3s are associated with worse overall survival for neuroblastoma
Abstract
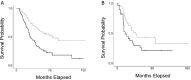
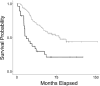
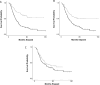
With the advent of large collections of adaptive immune receptor recombination reads representing cancer, there is the opportunity to further investigate the adaptive immune response to viruses in the cancer setting. This is a particularly important goal due to longstanding but still not well-resolved questions about viral etiologies in cancer and viral infections as comorbidities. In this report, we assessed the T cell receptor complementarity determining region-3 (CDR3) amino acid (AA) sequences, for blood-sourced TCRs from neuroblastoma (NBL) cases, for exact AA sequence matches to previously identified anti-viral TCR CDR3 AA sequences. Results indicated the presence of anti-viral TCR CDR3 AA sequences in the NBL blood samples highly significantly correlated with worse overall survival. Furthermore, the TCR CDR3 AA sequences demonstrating chemical complementarity to many cytomegalovirus antigens represented cases with a worse outcome, including cases where such CDR3s were obtained from tumor samples. Overall, these results indicate a significant need for, and provide a novel strategy for assessing viral infection complications in NBL patients.
Keywords: Anti-viral complementarity determining region-3; CMV; Co-morbidities; Neuroblastoma; T cell receptor.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have nothing to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Detection of Anti-CMV TCR CDR3s via Blood and Tumor Exome Files Correlates With Increased Survival for Stomach Adenocarcinoma and Soft Tissue Sarcoma.APMIS. 2025 Jul;133(7):e70053. doi: 10.1111/apm.70053. APMIS. 2025. PMID: 40653843
-
Delineation of a T-cell receptor CDR3-cancer mutanome aromaticity factor, assessable via blood samples, that facilitates the establishment of survival distinctions in bladder cancer.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Jul;149(8):4359-4366. doi: 10.1007/s00432-022-04339-w. Epub 2022 Sep 13. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36098856 Free PMC article.
-
Stratification of Wilms tumor patients using physicochemical properties of the adaptive immune receptor polypeptides, IGL and TRG.J Pediatr Urol. 2025 Feb;21(1):130-135. doi: 10.1016/j.jpurol.2024.10.012. Epub 2024 Oct 10. J Pediatr Urol. 2025. PMID: 39443216
-
High-dose chemotherapy and autologous haematopoietic stem cell rescue for children with high-risk neuroblastoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Oct 5;2015(10):CD006301. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006301.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26436598 Free PMC article.
-
High-dose chemotherapy and autologous haematopoietic stem cell rescue for children with high-risk neuroblastoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Aug 22;(8):CD006301. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006301.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Oct 05;(10):CD006301. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006301.pub4. PMID: 23970444 Updated.
Cited by
-
Chemical Complementarity of Blood-Sourced, Breast Cancer-Related TCR CDR3s and the CMV UL29 and IE1 Antigens is Associated with Worse Overall Survival.Biochem Genet. 2024 Oct 2. doi: 10.1007/s10528-024-10934-y. Online ahead of print. Biochem Genet. 2024. PMID: 39356353
References
-
- Bagaev DV, Vroomans RMA, Samir J, Stervbo U, Rius C, Dolton G, Greenshields-Watson A, Attaf M, Egorov ES, Zvyagin IV, Babel N, Cole DK, Godkin AJ, Sewell AK, Kesmir C, Chudakov DM, Luciani F, Shugay M (2020) VDJdb in 2019: database extension, new analysis infrastructure and a T cell receptor motif compendium. Nucleic Acids Res 48(D1):D1057–D1062. 10.1093/nar/gkz874 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chobrutskiy BI, Zaman S, Tong WL, Diviney A, Blanck G (2018) Recovery of T cell receptor V(D)J recombination reads from lower grade glioma exome files correlates with reduced survival and advanced cancer grade. J Neurooncol 140(3):697–704. 10.1007/s11060-018-03001-1 - PubMed
-
- Chobrutskiy BI, Chobrutskiy A, Zaman S, Yeagley M, Huda TI, Blanck G (2021) High-throughput, sliding-window algorithm for assessing chemical complementarity between immune receptor CDR3 domains and cancer mutant peptides: TRG-PIK3CA interactions and breast cancer. Mol Immunol 135:247–253. 10.1016/j.molimm.2021.02.026 - PubMed
-
- Chronister W, Sette A, Peters B (2022) Epitope-specific T cell receptor data and tools in the immune epitope database. Methods Mol Biol 2574:267–280. 10.1007/978-1-0716-2712-9_13 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

