Biosurfactant derived from probiotic Lactobacillus acidophilus exhibits broad-spectrum antibiofilm activity and inhibits the quorum sensing-regulated virulence
- PMID: 37421468
- PMCID: PMC10655870
- DOI: 10.17305/bb.2023.9324
Biosurfactant derived from probiotic Lactobacillus acidophilus exhibits broad-spectrum antibiofilm activity and inhibits the quorum sensing-regulated virulence
Abstract
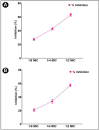
Antimicrobial resistance by pathogenic bacteria has become a global risk to human health in recent years. The most promising approach to combating antimicrobial resistance is to target virulent traits of bacteria. In the present study, a biosurfactant derived from the probiotic strain Lactobacillus acidophilus was tested against three Gram-negative bacteria to evaluate its inhibitory potential on their biofilms, and whether it affected the virulence factors controlled by quorum sensing (QS). A reduction in the virulence factors of Chromobacterium violaceum (violacein production), Serratia marcescens (prodigiosin production) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (pyocyanin, total protease, LasB elastase and LasA protease production) was observed at different sub-MIC concentrations in a dose-dependent manner. Biofilm development was reduced by 65.76%, 70.64% and 58.12% at the highest sub-MIC levels for C. violaceum, P. aeruginosa and S. marcescens, respectively. Biofilm formation on glass surfaces exhibited significant reduction, with less bacterial aggregation and reduced formation of extracellular polymeric materials. Additionally, swimming motility and exopolysaccharides (EPS) production were shown to be reduced in the presence of the L. acidophilus-derived biosurfactant. Furthermore, molecular docking analysis performed on compounds identified through gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) analysis of QS and biofilm proteins yielded further insights into the mechanism underlying the anti-QS activity. Therefore, the present study has clearly demonstrated that a biosurfactant derived from L. acidophilus can significantly inhibit virulence factors of Gram-negative pathogenic bacteria. This could provide an effective method to inhibit the formation of biofilms and QS in Gram-negative bacteria.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: Authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures











Similar articles
-
Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles Derived from Probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus (AgNPs-LR) Targeting Biofilm Formation and Quorum Sensing-Mediated Virulence Factors.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 May 31;12(6):986. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12060986. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37370305 Free PMC article.
-
Broad-spectrum quorum sensing and biofilm inhibition by green tea against gram-negative pathogenic bacteria: Deciphering the role of phytocompounds through molecular modelling.Microb Pathog. 2019 Jan;126:379-392. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2018.11.030. Epub 2018 Nov 23. Microb Pathog. 2019. PMID: 30476580
-
Lactiplantibacillus plantarum-Derived Biosurfactant Attenuates Quorum Sensing-Mediated Virulence and Biofilm Formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Chromobacterium violaceum.Microorganisms. 2022 May 13;10(5):1026. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10051026. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35630468 Free PMC article.
-
Sesamin and sesamolin rescues Caenorhabditis elegans from Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection through the attenuation of quorum sensing regulated virulence factors.Microb Pathog. 2021 Jun;155:104912. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2021.104912. Epub 2021 Apr 28. Microb Pathog. 2021. PMID: 33932548 Review.
-
Postbiotics as candidates in biofilm inhibition in food industries.Lett Appl Microbiol. 2024 Apr 8;77(4):ovad069. doi: 10.1093/lambio/ovad069. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 37309029 Review.
Cited by
-
Quercetin Exhibits Broad-Spectrum Antibiofilm and Antiquorum Sensing Activities Against Gram-Negative Bacteria: In Vitro and In Silico Investigation Targeting Antimicrobial Therapy.Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2025 Mar 30;2025:2333207. doi: 10.1155/cjid/2333207. eCollection 2025. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40196379 Free PMC article.
-
Lactobacillus acidophilus-Derived Cell-Free Supernatant Augments Methylene Blue-Mediated Photodynamic Inactivation Efficacy Against Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Planktonic Suspension and Biofilms.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025 May 22. doi: 10.1007/s12602-025-10558-7. Online ahead of print. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025. PMID: 40402416
-
Cutting-edge perspectives on biosurfactants: implications for antimicrobial and biomedical applications.3 Biotech. 2024 Dec;14(12):297. doi: 10.1007/s13205-024-04146-9. Epub 2024 Nov 11. 3 Biotech. 2024. PMID: 39539528 Review.
-
Antibacterial activity of bioemulsifiers/biosurfactants produced by Levilactobacillus brevisS4 and Lactiplantibacillus plantarumS5 and their utilization to enhance the stability of cold emulsions of milk chocolate drinks.Food Sci Nutr. 2023 Oct 10;12(1):141-153. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3740. eCollection 2024 Jan. Food Sci Nutr. 2023. PMID: 38268904 Free PMC article.
-
Biosurfactants as next-generation antimicrobials: mechanistic insights and applications in antibiofilm strategies for combatting antimicrobial resistance.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Sep 1. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04546-5. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40888881 Review.
References
-
- Dzobo K. The role of natural products as sources of therapeutic agents for innovative drug discovery. Compr Pharmacol. 2022:408–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-820472-6.00041-4.
-
- Yuan H, Ma Q, Ye L, Piao G. The traditional medicine and modern medicine from natural products. Molecules. 2016;21(5):559. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21050559. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Azeem M, Hanif M, Mahmood K, Ameer N, Chughtai FRS, Abid U. An insight into anticancer, antioxidant, antimicrobial, antidiabetic and anti-inflammatory effects of quercetin: a review. Polym Bull. 2023;80(1):241–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-022-04091-8. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lu L, Hu W, Tian Z, Yuan D, Yi G, Zhou Y, et al. Developing natural products as potential anti-biofilm agents. Chin Med. 2019;14(1):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13020-019-0232-2. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rutherford ST, Bassler BL. Bacterial quorum sensing: its role in virulence and possibilities for its control. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2012;2(11):a012427. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a012427. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

